Ambulatory Patient Group (APG) Implementation
Ambulatory Care Payment Reform
- Presentation is alos available in Portable Document Format (PDF)
Introduction and Overview
Background
- Existing Medicaid outpatient rate methodologies are broken, most payments are capped and ambulatory surgery rates are outdated.
- For example, most hospital clinic rates are capped at $67.50 plus capital resulting in a fixed payment methodology which fails to recognize variation in service intensity thereby discouraging the provision of higher intensity care.
- By failing to keep pace with the cost of care and medical advances, the current ambulatory care rates do not appropriately pay providers who deliver evidenced-based, state of the art care.
- New York´s growing budget deficit will require significant gap closing measures.
- The State´s almost $50 billion Medicaid program drives nearly 30% of General Fund spending.
- Ambulatory investments are made possible only through the reallocation of funds drawn from inpatient reform and rebasing.
- Payment restructuring coupled with targeted primary care enhancements are central to Medicaid reform.
Reform Objectives
- Encourage migration of services from inpatient to ambulatory/primary care settings.
- Invest in ambulatory care to provide more adequate reimbursement.
- Develop a new payment system to pay more for higher cost services and less for lower cost services.
- Ensure better payment homogeneity for similar/comparable services across ambulatory care settings.
- Improved clarity and transparency of payment structure and methodology.
- Frequent payment updates to recognize medical advances and changes in cost-of-service delivery.
- Support evidenced-based, state-of-the-art healthcare.
APG´s Fiscal Benefits
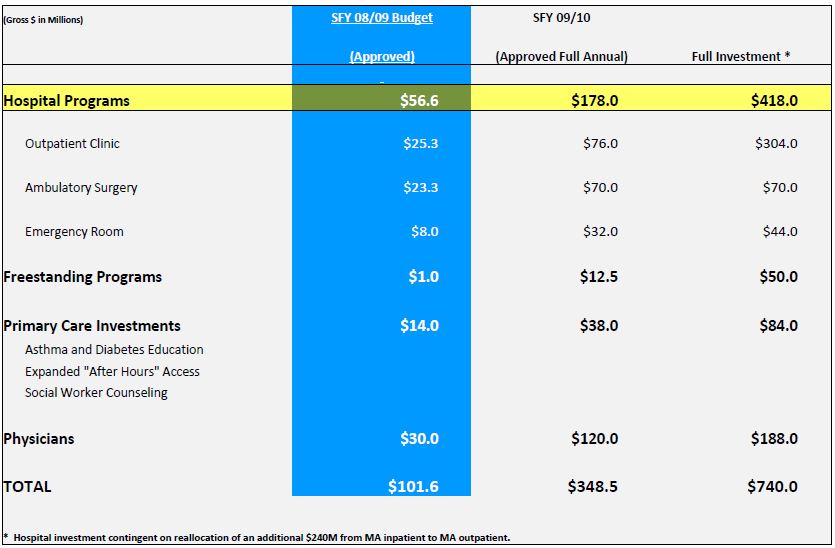
- $57M investment for hospitals in SFY 08/09.
- $178M full annual investment in SFY 09/10.
- Growing to $418M by year four (requires inpatient rebasing and reinvestment).
- For OPD, AS, and ED combined, average year one increase per visit is $45. Average year four increase per visit is $103.
- Average percentage increase in payment of 40% in year one. Average year four increase in payment of 90%.
- Assuming constant volume, average year one ambulatory payment increase of $850,000 per hospital (full annual). Average year four increase of $1,940,000 per hospital.
APG´s Clinical Strengths
- Superior to "Threshold Visit" and outdated PAS rates.
- Payment varies based on service intensity.
- Payment homogeneity for comparable services across ambulatory care settings (i.e., OPD, Amb Surg, ED, DTC).
- Emphasizes diagnosis and procedures over service volume.
APG´s Methodological Advantages
- Recognized and tested payment system.
- Enables prospective pricing for Ambulatory Care.
- Grouping and payment logic similar to DRGs.
- Uses standard HIPAA-compliant code sets (HCPCS and ICD-9 codes)
- Uses current HIPAA compliant claim formats.
- Greater clarity and transparency of payment structure and methodology.
- Features more frequent payment updates to:
- Better acknowledge the impact of medical advances, and
- Accommodate changes in service delivery patterns.
- Four year transition using "blend" to allow time to adjust to new payment methodology.
APG Timeline
- Hospital Provider Training - June /July 2008
- Draft APG Regulations - June 30, 2008
- State Plan Amendment to CMS - June 30, 2008
- Final APG Grouper/Pricer - July 11, 2008
- Interface Specs/Remit Specs - July 13, 2008
- Begin Hospital Provider Testing with eMedNY - September 5, 2008
- Freestanding D&TC and Amb Surg Provider Training - October 2008
- CMS Approval of SPA by December 1, 2008
- Implement APGs in Hospital-based OPDs and Amb Surg - December 1, 2008
- Begin D&TC / Freestanding Amb Surg Testing with eMedNY - December 2008
- Implement Hospital-based ED APGs - January 1, 2009
- Implement Primary Care Enhancements - Jauary 1, 2009
- Implement Freestanding D&TCs and Amb Surg APGs - March 1, 2009
APG Impact on Selected Procedures (Full Implementation)
Outpatient Department
| Proc Code | Procedure Description | EAPG | EAPG Description | Current Operating Payment | APG Operating Payment | Difference ($) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95071 | Bronchial Allergy Test | 116 | Allergy Tests | $67.50 | $292.54 | $225.04 | 333% |
| 99215 | Office/Outpatient Visit | 8711 | Signs, Symptoms and Other Factors Influencing Health | $67.50 | $152.40 | $84.90 | 126% |
| 97001 | Physical Therapy Eval | 271 | Physical Therapy | $67.50 | $64.10 | ($3.40) | −5% |
| 90669 | Pneumococcal Vaccine | 415 | Level II Immunization | $67.50 | $30.43 | ($37.07) | −55% |
Emergency Room
| Proc Code | Procedure Description | EAPG | EAPG Description | Current Operating Payment | APG Operating Payment | Difference ($) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37201 | Transcatheter therapy infuse | 111 | Pharmacotherapy Except by Extended Infusion | $150.00 | $224.42 | $74.42 | 50% |
| 99283 | Emergency Dept. Visit | 6042 | Chest Pain | $150.00 | $348.78 | $198.78 | 133% |
Ambulatory Surgery
| Proc Code | Procedure Description | EAPG | EAPG Description | All Inclusive Price3 | APG Operating Payment | Difference ($) | Difference (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31545 | Laryngoscopy, Direct | 63 | Level II Endoscopy Of The Upper Airway | $682.95 | $1,937.49 | $1,254.54 | 184% |
| 57505 | Endocervical Curettage | 196 | Level I Female Reproductive Procedures | $713.47 | $1,193.19 | $479.72 | 67% |
NOTE: APG payment shown is based on draft weights and base rates and is subject to revision.
1. Procedure Code was accompanied with primary diagnosis code 78096: generalized pain. 1
2. Procedure Code was accompanied with primary diagnosis code 78650: chest pain (NOS). 2
3. Ambulatory Surgery all inclusive prices include capital and are NYC area prices. Add apx. $150 to APG operating payment for capital. 3
APCs vs. APGs: Key Differences
| APCs | APGs | |
|---|---|---|
| Methodology | Primarily a payment classification system and fee schedule of individual outpatient procedures/services | Outpatient visit classification system, which places patients and services into clinically coherent groups |
| Efficiency | Minimal packaging of ancillaries and bundling of procedures | Comprehensive packaging and bundling |
| Comprehensiveness | Excludes many services, which are then covered under other fee schedules | Covers all medical outpatient services |
| Medical Payment Basis | Medical APCs pay based on self-reported effort (duration of patient contact) | Medical APGs pay based on patient´s condition and service intensity (i.e., diagnosis and procedure) |
| Setting and Scope | Applicability limited to payment for facility cost for hospital based outpatient services and ambulatory surgery centers | Broader applicability to other services and settings (e.g., Mental Hygiene, Physical Therapy, and Occupational Therapy) and to performance reporting |
| Unit of Service | Payment structure based on utilization by procedure (volume) | Payment structure based on visits (service mix) |
According to CMS, APCs have moved from packaged encounter-based payment to inefficient service-level payment
- "… over the past 7 years, significant attention has been concentrated on service specific payment for services furnished to particular patients, rather than on creating incentives for the efficient delivery of services through encounter or episode-of-care-based payment."
- "Overall packaging included in the clinical APCs has decreased, and the procedure groupings have become smaller as the focus has shifted to refining service-level payment."
- " Specifically, in the CY 2003 OPPS, there were 569 APCs, but by CY 2007, the number of APCs had grown to 862, a 51 percent increase in 4 years."
Federal Register / Vol. 72, No. 148 / Thursday, August 2, 2007 / Proposed Rules
CMS believes packaging and bundling provides flexibility and creates efficiency
- "Packaging and bundling payment for multiple interrelated services into a single payment creates incentives for providers to furnish services in the most efficient way by enabling hospitals to manage their resources with maximum flexibility…"
- "In many situations, the final payment rate for a package of services may do a better job of balancing variability in the relative costs of component services compared to individual rates covering a smaller unit of service without packaging and bundling."
- CMS´s new Composite APCs will bundle and package more services:
- "… it would be more appropriate to establish a composite APC under which we would pay a single rate for the service reported with a combination of HCPCS codes on the same date of service … than to continue to pay for these individual services under service specific APCs."
Federal Register / Vol. 72, No. 148 / Thursday, August 2, 2007 / Proposed Rules
Scope of APG Services
- APGs, in the initial phase, will cover the following services:
- General Clinic
- Specialty Clinic (HIV/AIDS, Renal, Oncology, PCAP)
- Emergency Department
- Ambulatory Surgery
- APGs, in the initial phase, will not cover:
- Mental Hygiene
- Other Managed Care FFS Carve Outs (e.g., school based health)
- Ordered Ambulatory Services
- FQHCs that do not opt-into APGs
APG Enabling Statute Summary
| Start Date | Phase | Operating Rate | Capital Add-on | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospital Programs | ||||
| Ambulatory Surgery Art. VII Section 18 (c) |
Dec. 1, 2008 | 100% | Full APG payment | Downstate/Upstate |
| Emergency Room Art. VII Section 18 (d) |
Jan. 1, 2009 | 100% | Full APG Payment | Facility Specific |
| Outpatient Clinic Art. VII Section 18 (a) |
Dec. 1, 2008 | 25% | Year 1 Blend APG Payment (25%) and Avg. Per Visit CY 2007 (75%) |
Facility Specific |
| Freestanding Programs | ||||
| Freestanding Clinic (D&TC´s) Art. VII Section 18 (b) |
Mar. 1, 2009 | 25% | Year 1 Blend APG Payment (25%) and Avg. Per Visit CY 2007 (75%) |
Facility Specific |
| Ambulatory Surgery Centers Art. VII Section 18 (b) |
Mar. 1, 2009 | 25% | Same Blend as Above | Downstate/Upstate |
Total Ambulatory Care Investment Package
Primary Care Enhancements
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| Diabetes/Asthma Education Art. VII Section 18 (f) (ii) (A) | Establish coverage for diabetes and asthma education by certified educators in clinic and office-based settings. |
| Expanded ´After Hours´ Access Art. VII Section 18 (f) (ii) (B) | Provide enhanced payment for expanded ´after hours´ access in both clinic and office-based settings. |
| Social Worker Counseling Art. VII Section 18 (f) (ii) C | Reimburse for individual psychotherapy services provided by a social worker for children, adolescents, and pregnancy related counseling. |
| Smoking Cessation | Reimburse for pregnant women in the clinic or the office. Must be provided with a medical visit. |
3M™ Enhanced Ambulatory Patient Grouping System
Business Performance
Solutions & Changing Technology
Outline
Definition of the Classification System
- DRGs and EAPGs
- EAPGs and APCs
Grouping Under EAPGs
- Procedure Groups
- Medical Visits
Standard & Enhanced Features
- Consolidation
- Packaging
- Discounting
- Per-Diems
- Modifiers
- User Options
Enhanced Ambulatory Patient Groups (EAPGs)
A Definition
EAPGs are a patient classification system designed to explain the amount and type of resources used in an ambulatory visit. Patients in each EAPG have similar clinical characteristics and similar resource use and cost.
EAPGs were developed to encompass the full range of Ambulatory settings including same day surgery units, hospital emergency rooms, and outpatient clinics.
EAPGs can not address nursing home services, inpatient services or miscellaneous services like transportation.
EAPGs developed to represent ambulatory patient across entire patient population, not just Medicare.
Visit based
- Based on the ambulatory visit
- Visit has many definitions
- Generally as reported on the claim as submitted
- EAPGs allow for segregation of multiple visits reported on a single claim based on line item dates of service
EAPGs vs DRGs
- DRGs
- Describes an inpatient admission
- Uses discharge date to define code sets
- Based only on ICD-9-CM codes
- Each admission assigned only 1 DRG
- EAPGs
- Defines ambulatory visit
- Uses date of service to define code sets
- Based on ICD-9-CM Dx and HCPCS Px codes
- Multiple EAPGs may be assigned per visit
EAPGs vs APCs: grouping
| Category | APCs | EAPGS |
|---|---|---|
| Number of groupings | 802 APC groups
|
467 EAPG groups
|
Editing
|
Extensive edits – 78 OCE edits |
Almost no editing by grouper
|
| Modifiers | Extensive use in editing (e.g., for CCI) Subset for grouping/payment |
Enhancement Feature Smaller subset & purpose (25, 27, 52, 73, 59, 50) |
APGs vs APCs: grouping; p2
| Category | APCs | EAPGS |
|---|---|---|
| Status indicators | Used for type of service Examples:
|
´Type´ indicates type of service (No fee schedule) Significant procedures Ancillary procedures Incidental procedures Medical visit |
| Categories | None | Similar to MDCs - 54 EAPG categories Examples:
|
| Packaging | Standard packaging - - status indicator N Conditional packaging - recent introduction |
Extensive
|
Data set for defining EAPGs
- EAPG
- ICD-9-CM diagnosis (Dx) codes
- HCPCS level I & level II procedure (Px) codes
- HCPCS level I modifiers
- 25 distinct service
- 27 multiple E/M visits, same date
- 52 terminated ("reduced") px
- 73 terminated px
- 59 separate px
- 50 bilateral px
- Gender
Outputs
- EAPG groups
- EAPG types
- EAPG categories
- Flags used for determining payment e.g.:
- Consolidation
- Packaging
- Discounting
- Etc.
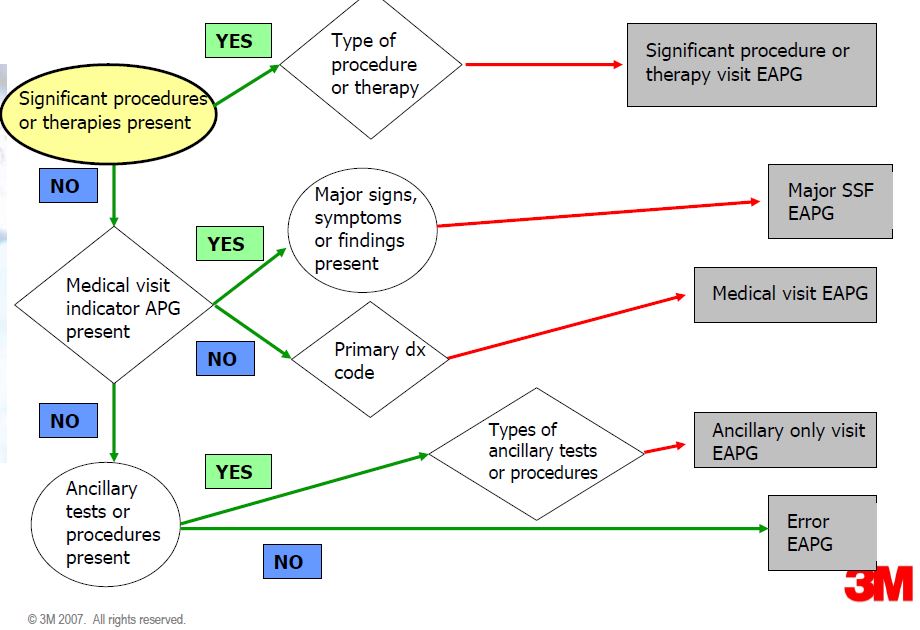
Three Types of Procedures in the EAPG System
SIGNIFICANT PROCEDURES: Normally scheduled, constitutes the reason for the visit and dominates the time and resources expended during the visit
Example: excision of skin lesion, stress tests
ANCILLARY TESTS AND PROCEDURES: Ordered by the primary physician to assist in patient diagnosis or treatment
Example: immunizations, plain films, laboratory tests
INCIDENTAL PROCEDURE: An integral part of a medical visit and is usually associated with professional services
Example: range of motion measurements
EAPG logic
Significant Procedure Consolidation
- Definition: When a patient has multiple significant procedures, some of the significant procedures may require minimal additional time or resources. Significant procedure consolidation refers to the collapsing of multiple related significant procedure EAPGs into a single EAPG for the purpose determining the payment.
- Example: If both a Level I incision and an Level II incision are coded on a patient bill, only the Level II skin incision will be used in the EAPG payment computation.
- Types of consolidation
- Multiple same procedure or APG
- Clinical (based on clinical algorithm)
Example of Significant Procedure Consolidation
| CPT | EAPG | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Assigned | EAPG Description | Action |
| 11406 | 010 | Level II excision and biopsy of skin and soft tissue | Consolidate with EAPG 137 |
| 11404 | 009 | Level I excision and biopsy of skin and soft tissue | Consolidate with EAPG 137 |
| 11400 | 009 | Level I excision and biopsy of skin and soft tissue | Consolidate with EAPG 137 |
| 45385 | 137 | Therapeutic colonoscopy | Include in payment |
| 45378 | 137 | Therapeutic colonoscopy | Consolidate with EAPG 137 |
| 45330 | 132 | Anoscopy with biopsy and diagnostic proctosigmoidoscopy | Include in payment |
Medical EAPGs
Describe patients who receive medical treatment but do not have a significant procedure performed during the visit.
Medical patients are described using the diagnoses of the patient coded in ICD-9-CM.
Medical visit EAPG
- Assigned based on primary dx code
- UB-04 form locator 67 (field attributes: 1 field; 1 line)
- X12, 837
- Loop ID - 2300; Reference Indicator - H101-C022-02; X12 Element # - 1271; Data Element Qualifier - 1270-BK or ABF for ICD10
- Definition: "The ICD-9-CM codes describing the principal diagnosis (i.e., the condition established after study to be chiefly responsible for occasioning the admission of the patient for care." (UB-04 Data Specifications Manual, NUBC)
- Requires a medical visit indicator code
- E&M CPT code
- The medical visit EAPG is assigned to the E&M code
Modifiers Used in Enhanced APGs
- 25 distinct service
- Allows assignment of a medical visit EAPG on the same claim/day as a significant procedure EAPG (Significant Procedure + Distinct and Separate Medical Visit)
- 27 multiple E&M encounters
- Allows assignment of additional medical visit/services ancillary EAPG (Medical Visit + Distinct and Separate Medical Visit)
- 52 & 73 terminated procedure
- Flags a procedure code for discounting
- 59 separate procedure
- Turns off consolidation - allows separate payment
- 50 bilateral procedure
- Flags a code for additional payment (150%)
Medical & procedure EAPG on same day
- Medical EAPG and significant procedure EAPG allowed on same day with modifier 25 (new to version 3.)
- Modifier 25 must be coded on medical visit indicator code (E&M CPT code)
- Multiple medical visits on same day
- One medical EAPG is assigned - based on the PDX
- Additional E&M codes with modifier 27 are assigned to ancillary EAPG (additional medical visits/services) and paid
- Additional MVI/E&M without modifier 27 remain incidental and are packaged
- Multiple medical visits on separate days
- Each paid if separate E&M is coded each day
- Each would receive the same final medical EAPG (based on primary dx)
Ancillary Packaging
- A patient with a significant procedure or a medical visit may have ancillary services performed as part of the visit. Ancillary packaging refers to the inclusion of certain ancillary services into the EAPG payment for a significant procedure or medical visit. A uniform list of ancillary EAPGs that are always packaged into a significant procedure or medical visit was developed.
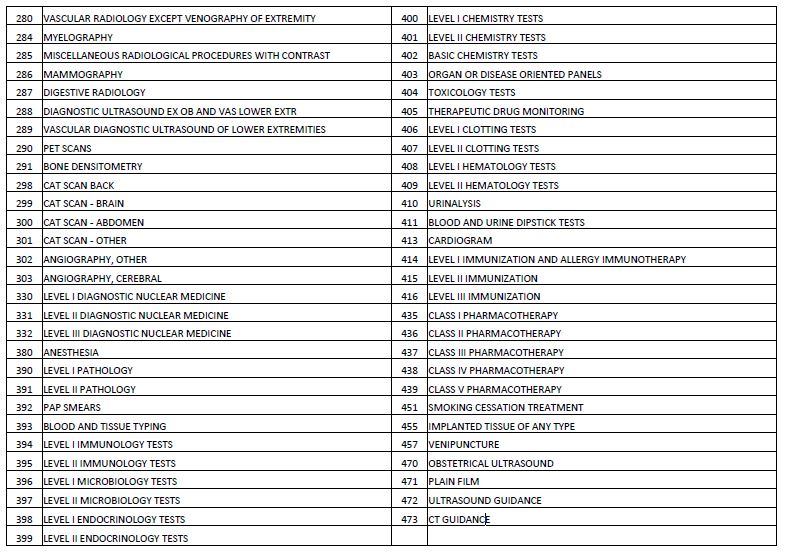
Uniform Packaging List
| EAPg | EAPG Description |
|---|---|
| 380 | ANESTHESIA |
| 390 | LEVEL I PATHOLOGY |
| 394 | LEVEL I IMMUNOLOGY TESTS |
| 396 | LEVEL I MICROBIOLOGY TESTS |
| 398 | LEVEL I ENDOCRINOLOGY TESTS |
| 400 | LEVEL I CHEMISTRY TESTS |
| 402 | BASIC CHEMISTRY TESTS |
| 406 | LEVEL I CLOTTING TESTS |
| 408 | LEVEL I HEMATOLOGY TESTS |
| 410 | URINALYSIS |
| 411 | BLOOD AND URINE DIPSTICK TESTS |
| 412 | SIMPLE PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS |
| 413 | CARDIOGRAM |
| 423 | INTRODUCTION OF NEEDLE AND CATHETER |
| 424 | DRESSINGS AND OTHER MINOR PROCEDURES |
| 425 | OTHER MISCELLANEOUS ANCILLARY PROCEDURES |
| 426 | PSYCHOTROPIC MEDICATION MANAGEMENT |
| 427 | BIOFEEDBACK AND OTHER TRAINING |
| 435 | CLASS I PHARMACOTHERAPY |
| 471 | PLAIN FILM |
Example of Ancillary Packaging
| CPT Code |
EAPG Assigned |
EAPG Description | Action |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11406 | 010 | Level II excision and biopsy of skin and soft tissue | Consolidate with EAPG 137 |
| 45385 | 137 | Therapeutic colonoscopy | Include in payment |
| 88304 | 390 | Level I pathology | Package |
| 82947 | 402 | Basic chemistry tests | Package |
| 84233 | 399 | Level II endocrinology tests | Include in payment |
| 93000 | 413 | Cardiogram | Package |
Multiple Significant Procedure Discounting
- When multiple significant procedures or therapies are performed, a discounting of the EAPG payment is applied. Discounting refers to a reduction in the standard payment rate for an EAPG. Discounting recognizes that the marginal cost of providing a second procedure to a patient during a single visit is less than the cost of providing the procedure by itself.
Example of APG Payment
| CPT Code | EAPG Assigned | EAPG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Payment Discount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31545 | 063 | Level II Endoscopy of Upper Air Way | Significant Procedure | Full Payment | 100% |
| 31515 | 062 | Level I Endoscopy of Upper Air Way | Related Procedure | Consolidated | 0% |
| 42405 | 252 | Level I Facial and ENT Procedures | Unrelated Procedure | Discounted | 50% |
| 88331 | 390 | Level I Pathology | Routine Ancillary | Packaged | 0% |
| 82435 | 402 | Basic Chemistry Tests | Routine Ancillary | Packaged | 0% |
| 93000 | 413 | Cardiogram | Routine Ancillary | Packaged | 0% |
| 00322 | 380 | Anesthesia | Routine Ancillary | Packaged | 0% |
| 84233 | 399 | Level II Endocrinology Tests | Non Routine Ancillary | Full Payment | 100% |
Additional topics
- Inpatient only list
- Core set of codes defined
- User may add to list
- Per diem
- Partial Hospital Programs (e.g., for mental illness or drug abuse)
- Full-day or half-day
- Partial Hospital Programs (e.g., for mental illness or drug abuse)
- Two types of per diem assignment
- Direct from HCPCS code
- Indirect from two clinical lists
- Two fixed clinical lists created for use in defining per diem payments
- Error EAPG
- Single error EAPG - 999
- Unassigned flag indicates the reason EAPG is not assigned
- 2 = Inpatient procedure
- 3 = Invalid procedure code
- 6 = E-code dx for medical visit
Access to EAPG Definitions Manual
- The EAPG Definitions Manual is available at no cost from the 3M Definitions Manual Website. The link is
- http://solutions.3m.com/wps/portal/3M/en_US/3M_Health_Information_ Systems/HIS/Products/Definition_Manuals/
- Click on New York Customers Only portal (highlighted in red)
- Download, complete, and sign the one page Order Form-- and send back to 3M
- You will receive access instructions in 2-3 working days and be able to download the Definitions Manual
- Definitions Manual will be kept current with each update to the EAPG software
- The Manual will be available at no cost thru 12/31/08
APG Payment Methodology and Payment Examples
Sample APG / HCPCS Crosswalk
| APGs | APG Descp | HCPCS Code | HCPCS Descp |
|---|---|---|---|
| 84 | DIAGNOSTIC CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION | 93501 | Right heart catheterization |
| 93510 | Left heart catheterization | ||
| 93511 | Left heart catheterization | ||
| 93514 | Left heart catheterization | ||
| 93524 | Left heart catheterization | ||
| 93526 | Rt & Lt heart catheters | ||
| 93527 | Rt & Lt heart catheters | ||
| 93528 | Rt & Lt heart catheters | ||
| 93529 | Rt, lt heart catheterization | ||
| 93530 | Rt heart cath, congenital | ||
| 93531 | R & l heart cath, congenital | ||
| 93532 | R & l heart cath, congenital | ||
| 93533 | R & l heart cath, congenital | ||
| S8093 | CT angiography coronary |
Sample APGs and Preliminary Weights
Draft Only - Weights Subject to Change
| EAPG | EAPG Name |
Type | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|
| 030 | LEVEL I MUSCULOSKELETAL PROCEDURES EXCLUDING HAND AND FOOT | Significant Procedure | 5.1262 |
| 031 | LEVEL II MUSCULOSKELETAL PROCEDURES EXCLUDING HAND AND FOOT | Significant Procedure | 6.4128 |
| 032 | LEVEL III MUSCULOSKELETAL PROCEDURES EXCLUDING HAND AND FOOT | Significant Procedure | 8.0977 |
| 040 | SPLINT, STRAPPING AND CAST REMOVAL | Significant Procedure | 1.2740 |
| 084 | DIAGNOSTIC CARDIAC CATHETERIZATION | Significant Procedure | 7.7960 |
| 112 | PHLEBOTOMY | Significant Procedure | 0.3295 |
| 116 | ALLERGY TESTS | Significant Procedure | 2.0745 |
| 271 | PHYSICAL THERAPY | Significant Procedure | 0.4134 |
| 280 | VASCULAR RADIOLOGY EXCEPT VENOGRAPHY OF EXTREMITY | Significant Procedure | 7.6514 |
| 315 | COUNSELING OR INDIVIDUAL BRIEF PSYCHOTHERAPY | Significant Procedure | 0.1797 |
| 396 | LEVEL I MICROBIOLOGY TESTS | Ancillary | 0.1574 |
| 397 | LEVEL II MICROBIOLOGY TESTS | Ancillary | 0.5223 |
| 413 | CARDIOGRAM | Ancillary | 0.2863 |
| 414 | LEVEL I IMMUNIZATION AND ALLERGY IMMUNOTHERAPY | Ancillary | 0.1301 |
| 471 | PLAIN FILM | Ancillary | 0.3400 |
| 527 | PERIPHERAL NERVE DISORDERS | Medical Visit | 0.7778 |
| 562 | INFECTIONS OF UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT | Medical Visit | 0.6313 |
| 575 | ASTHMA | Medical Visit | 0.9495 |
| 599 | HYPERTENSION | Medical Visit | 0.6073 |
| 826 | ACUTE ANXIETY & DELIRIUM STATES | Medical Visit | 0.6987 |
| 808 | VIRAL ILLNESS | Medical Visit | 0.7791 |
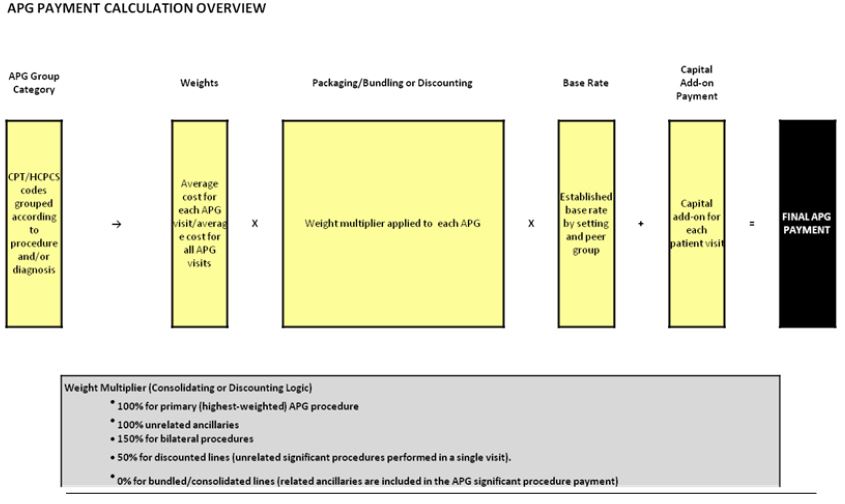
APG Payment Definitions
- Consolidation (a.k.a., "Bundling") - The inclusion of payment for a related procedure in the payment for a more significant procedure provided during the same visit.
- Packaging - The inclusion of payment for related ancillary services in the payment for a significant procedure or medical visit.
- The majority of "Level 1 APGs" are packaged in New York State.
- Discounting - A discounted payment for an additional, but unrelated, procedure provided during the same visit to acknowledge cost efficiencies.
APG Payment Methodology
APG Example 1 – Medical Visit
(All procedures are grouped based on the same Date of Service)
| Medical Visit (COPD) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPT Code | CPT Description | APG | APG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Full APG Weight | Percent Paid | Allowed APG Weight | Sample Base Rate | Paid Amount |
| 99213 | E & M, est. pt., low complexity (15 mins.) | 574 | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | Medical Visit | Full Payment | 1.1096 | 100% | 1.1096 | $148 | $ 164 |
| 82565 | Creatinine, blood | 400 | Level I Chemistry Tests | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.1266 | 0% | 0.0000 | $148 | $ ‐ |
| 71020 | Radiologic, chest, two views, frontal and lateral | 471 | Plain Film | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.6717 | 0% | 0.0000 | $148 | $ ‐ |
| Operating Totals | 1.9079 | 1.1096 | $ 164 | |||||||
| Capital Add‐On | $ 15 | |||||||||
| Total Payment | $ 179 | |||||||||
Note: All procedures shown were performed on the same date of service, per the APG definition of a visit.
Note: APG weights and base rates shown are for illustrative purposes only.
APG Example 2 – Medical Visit
(All procedures are grouped based on the same Date of Service)
| HIV/AIDS Routine Visit (Equivalent to 7 Tier ‐ Low Intensity) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPT Code | CPT Description | APG | APG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Full APG Weight | Percent Paid | Allowed APG Weight | Sample Base Rate | Paid Amount |
| 99213 | E & M, est. pt., low complexity (15 mins.) | 881 | AIDS | Medical Visit | Full Payment | 1.2202 | 100% | 1.2202 | $148 | $ 181 |
| 85025 | CBC w/diff | 408 | Level I Hematology Tests | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.1334 | 0% | 0.0000 | $148 | $ ‐ |
| 80076 | Hepatic function panel | 403 | Organ or Disease Oriented Panels | Ancillary | Full payment | 0.3269 | 100% | 0.3269 | $148 | $ 48 |
| 90740 | Hepatitis B vaccinations | 416 | Level III Immunizations | Ancillary | Full Payment | 0.4420 | 100% | 0.4420 | $148 | $ 65 |
| 36415 | Venipuncture | 457 | Venipuncture | Ancillary | Full Payment | 0.2674 | 100% | 0.2674 | $148 | $ 40 |
| Operating Totals | 2.3899 | 2.2565 | $ 334 | |||||||
| Capital Add‐On | $ 15 | |||||||||
| Total APG Payment | $ 349 | |||||||||
Note: APG weights and base rates shown are for illustrative purposes only. The primary diagnosis was AIDS (ICD-9 042). For this visit, the following carved-out services were billed to the Laboratory Fee Schedule: 87900 ($80), 87901 ($350), and 87903 ($675).
APG Example 3 – Ambulatory Surgery
(All procedures are grouped based on the same Date of Service)
| Gynecology/Obstetrics Visit | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPT Code | CPT Description | APG | APG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Full APG Weight | Percent Paid | Allowed APG Weight | Sample Base Rate | Paid Amount |
| 57505 | Endocervical curettage | 196 | Level I Female Reproductive Procd | Significant Procedure | Full payment | 6.4150 | 100% | 6.4150 | $186 | $1,193 |
| 87490 | Chlamydia trachomatis, direct probe technique | 394 | Level I Immunology Tests | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.1638 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 87590 | Neisseria gonorrhea, direct probe technique | 397 | Level II Microbiology Tests | Ancillary | Full payment | 0.2597 | 100% | 0.2597 | $186 | $ 48 |
| 88305 | Level IV Surgical pathology, gross and microscopic examination | 390 | Level I Pathology | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.4783 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 99215 | Office or other outpatient visit | 491 | Medical Visit Indicator | Incidental | Packaged | 1.4099 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| Operating Totals | 8.7267 | 6.6747 | $ 1,241 | |||||||
| Capital Add‐On | $ 151 | |||||||||
| Total Payment | $ 1,392 | |||||||||
Note: APG weights and base rates shown are for illustrative purposes only.
APG Example 4 – Ambulatory Surgery
(All procedures are grouped based on the same Date of Service)
| Ambulatory Surgery Visit | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPT Code | CPT Description | APG | APG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Full APG Weight | Percent Paid | Allowed APG Weight | Sample Base Rate | Paid Amount |
| 31545 | Laryngoscopy, direct, operative, with operating microscope or telescope | 063 | Level II Endoscopy of Upper Air Way | Significant Procedure | Full Payment | 10.4166 | 100% | 10.4166 | $186 | $1,937 |
| 31515 | Laryngoscopy, direct, with or without tracheoscopy | 062 | Level I Endoscopy of Upper Air Way | Related Procedure | Consolidated | 2.9928 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 42405 | Salivary gland and duct Incision | 252 | Level I Facial and ENT Procedures | Unrelated Procedure | Discounted | 4.7723 | 50% | 2.3862 | $186 | $ 444 |
| 88331 | Pathology consultation during surgery, first tissue block, with frozen section, single specimen | 390 | Level I Pathology | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.4783 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 82435 | Assay of blood chloride | 402 | Basic Chemistry Tests | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.0844 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 93000 | Cardiography, electrocard., routine ECG | 413 | Cardiogram | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.2748 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 00322 | Anesth, biopsy of thyroid | 380 | Anesthesia | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.4364 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 84233 | Receptor assay estrogen | 399 | Level II Endocrinology Tests | Ancillary | Full Payment | 0.2948 | 100% | 0.2948 | $186 | $ 55 |
| Operating Totals | 19.7504 | 13.0976 | $ 2,436 | |||||||
| Capital Add‐On | $ 151 | |||||||||
| Total Payment | $ 2,587 | |||||||||
Note: APG weights and base rates shown are for illustrative purposes only.
APG Example 5 – Emergency Department
(All procedures are grouped based on the same Date of Service)
| CPT Code | CPT Description | APG | APG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Full APG Weight | Percent Paid | Allowed APG Weight | Sample Base Rate | Paid Amount |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36556 | Insert non‐tunnel cv cath | 083 | Transvenous Catheter | Significant Procedure | Full Payment | 8.9572 | 100% | 8.9572 | $142 | $1,272 |
| 74150 | Ct abdomen w/o dye | 300 | Cat Scan ‐ Abdomen | Significant Procedure | Discounted | 1.3809 | 50% | 0.6905 | $142 | $ 98 |
| 72192 | Ct pelvis w/o dye | 301 | Cat Scan ‐ Other | Significant Procedure | Consolidated | 1.4780 | 0% | 0.0000 | $142 | $ ‐ |
| 83690 | Assay of lipase | 400 | Level I Chemistry Tests | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.1266 | 0% | 0.0000 | $142 | $ ‐ |
| 80053 | Comprehen metabolic panel | 403 | Organ or Disease Oriented Panels | Ancillary | Full Payment | 0.3269 | 100% | 0.3269 | $142 | $ 46 |
| J1170 | Hydromorphone injection | 435 | Class I Pharmacotherapy | Uniformly Pkgd Drug | Packaged | 0.2830 | 0% | 0.0000 | $142 | $ ‐ |
| J2405 | Ondansetron hcl injection | 435 | Class I Pharmacotherapy | Uniformly Pkgd Drug | Packaged | 0.2830 | 0% | 0.0000 | $142 | $ ‐ |
| 94760 | Measure blood oxygen level | 490 | Incidental to Medical Visit | Incidental | Packaged | 0.7535 | 0% | 0.0000 | $142 | $ ‐ |
| 99283 | Emergency dept visit | 491 | Medical Visit Indicator | Incidental | Packaged | 1.4099 | 0% | 0.0000 | $142 | $ ‐ |
| Operating Totals | 14.9990 | 9.9746 | $ 1,416 | |||||||
| Capital Add‐On | $ 22 | |||||||||
| Total Payment | $ 1,438 |
Note: APG weights and base rates shown are for illustrative purposes only.
EAPG Relative Weight Process
Presented by Treo Solutions
NYDOH Training Session
Six Basic Steps
- Define Data Set
- Cost Development
- Group Data
- Singletons
- Calculate Average Costs/Weights
- Validate
1. Define Data Set
- Define Data Set
- 2005 Hospital Outpatient MMIS data
- 2005 Referred Ambulatory MMIS data
- Determine Data Sources
- ER, Amsurg, and Hospital-based Clinic
- Determine Services to be Paid Under APGs
- First, includeclaims with approved rate codes from DOH.
- Then, excludelines outside the scope of EAPGs
- i.e. Per Diems, DME, etc.
2. Cost Development
- Determine Ratio of Cost to Charges (RCCs)
- From 2005 NYS Institutional Cost Report (ICR)
- By department for each hospital
- Map RCCs to each claim line by revenue code.
- If RCC was unavailable for revenue code, hospital´s overall RCC was used.
- Multiply line charges by RCC to determine cost.
- Remove any visit with line cost > $100,000
- Remove any visit with line cost < $1
3. Group Data
- Grouper divides each claim into visits based on date of service.
- Grouper assigns each line an APG based on CPT.
- For medical visits, the line CPT and the primary diagnosis are used to determine the line APG.
4. Select Singleton Visits
- Select single "service" visits from data set.
- Includes visits with packaged/RCO lines.
- Does not include visits with discounting/consolidation.
- Singleton visits provide the best estimate for average resource use by APG.
- Singleton visits also including cost estimates for packaged ancillary services and RCO lines that occur during a visit.
- Remove outlier visits for each APG (i.e., cost more than four standard deviations from the mean for each APG).
Singleton Examples
APG 146 - Level II Laproscopy
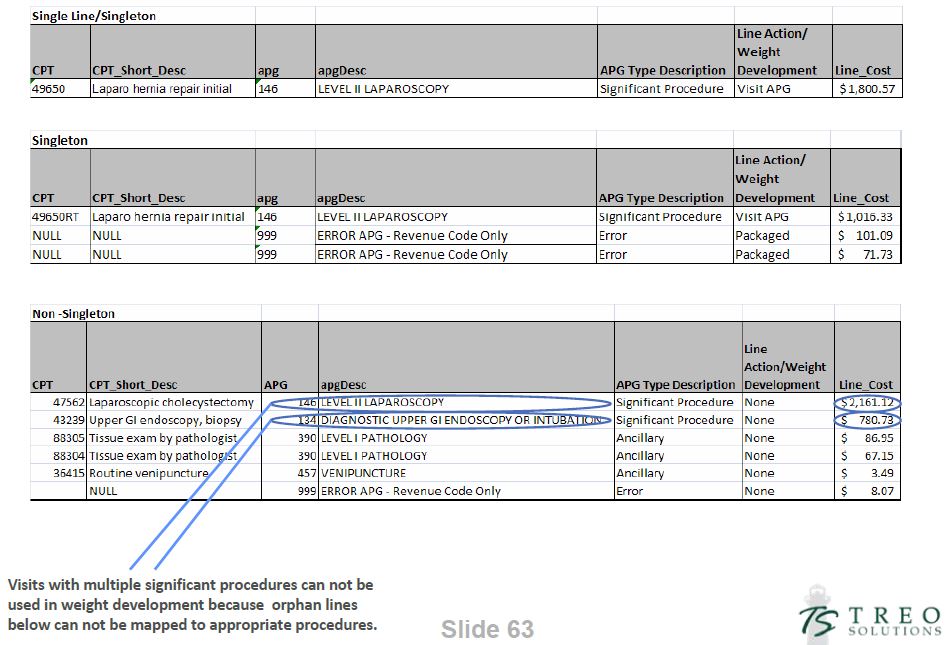
APG 574 - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
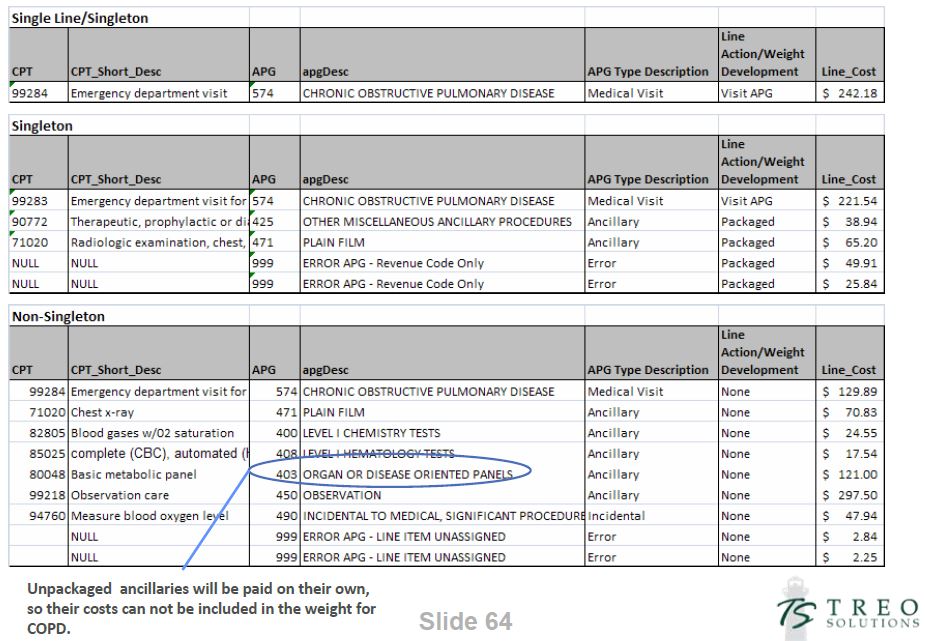
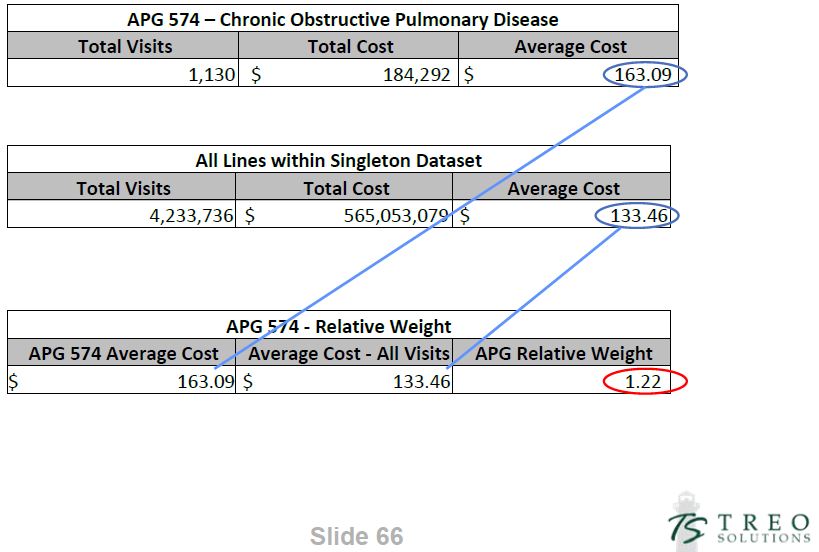
5. Calculate Relative Weights
- Relative Weight
- Measure of the resource intensity of an APG relative to other APGs in a specific data set.
- Determine Average Cost for Each EAPG
- = Σ of APG costs/ Σ of APG Visits
- Determine Average Cost for All EAPGs
- = Σ of all singleton costs/ Σ of all singleton visits
- Determine EAPG Relative Weight
- = APG Average Cost /Average Cost for all singletons
Relative Weight Example
6. Validate
- Benchmark Results:
- Null volume
- Low volume
- Single provider APGS
- Overall reasonableness of weights
- Data Sources:
- Meds II
- Referred Amb
- Referred Drug
- Treo Commercial
- Minimal claims affected through adjustments
APG Base Rate Development
APG Base Rates
- Base rates are established for peer groups based on one or more of the following factors:
- Service Type (OPD, ED, Amb Surg, Free-Standing Clinic, Free-Standing Amb Surg)
- Region (Upstate, Downstate)
- Procedure (Dental)
APG Base Rate Regions
- Downstate - New York City, Nassau, Suffolk, Westchester, Rockland, Putnam, Dutchess, Orange
- Upstate - The rest of the State
Base Rate Variables
- Case Mix Index (CMI)
- Coding Improvement Factor (CIF)
- Visit Volume
- Targeted Expenditure Level
- Base Year Expenditures
- Investment
- Reported Provider Cost by Peer Group (for scaling of investments)
Case Mix Index
- Definition - The average allowed APG weight per visit for a defined group of visits (based on peer group and time period of claims).
- Preliminary Statewide CMIs (used for budgetary approval - subject to revision)
- OPD - 1.44
- Amb Surg - 8.16
- Emergency Department - 1.52
Coding Improvement Factor
- A numeric value used to adjust for the fact that the coding of claims subsequent to the implementation of APGs will become more complete and accurate (CMIs will increase).
Base Year Visits and Payment
- 2005 is the base year for APG services implemented from December 1, 2008 through March 1, 2009.
- All revenues and visits for services moving to APG reimbursement will be used in the calculation, except that …
- "Visits" for Epogen (rate code 3106) are excluded from the calculation.
Investments Used in Base Rate Calculations
- Outpatient Department – $304 million*
- Ambulatory Surgery – $ 70 million
- Emergency Department – $ 32 million
* Assumes full reinvestment from inpatient rebasing by year four.
Base Rate Formula
(for initial implementation)
Base Year Expenditures + Investment
CMI × CIF × Base Year Visits
Sample Base Rate Calculation
Statewide OPD with Full Investment (for illustration purposes only - no such peer group exists)
(2005 Payment) (Investment)
$333,573,496 + $304,000,000
_____________________________________ = $137.40
1.4366 × 1.02 × 3,166,810
(CMI) (CIF) (2005 Visits)
Average Payment Per APG Visit = 1.4366 × 1.02 × $137.40 = $201
Current Operating Payment Per Visit = $105
Capital Add-Ons
- OPD and ED will have provider-specific per visit capital add-ons, consistent with current practice.
- Ambulatory Surgery, consistent with current practice, will have a per-visit price for capital. This price will vary by peer group but not procedure.
Reweighting/Rebasing Schedule
- APG relative weights will be updated at least annually to keep pace with medical advances and changes in service delivery patterns.
- Each time the relative weights are updated the base rate will also be revised.
- The 3M grouper / pricer software will be updated at least twice a year based on changes to the code sets and modifications to the NYS-specific APG methodology.
APG Phasing and Blending Methodology
Hospital OPD and DTC Transition and "Blend"
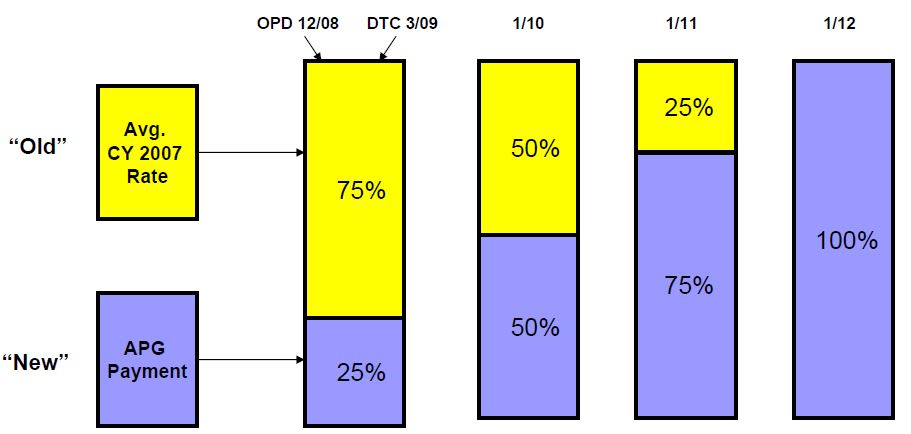
Ambulatory Surgery and Emergency Department will not be transitioned and instead will move to 100% APGs immediately, Amb Surg on 12/1/08 and ED on 1/1/09.
Calculation of the Existing Per-Visit Payment - for Purposes of Creating the Blend
- The "blend" applies only to OPD.
- Both Ambulatory Surgery and Emergency Department move to 100% APG payment upon implementation (no blend).
- Calculated using CY 2007 claims data.
- Frozen throughout the period of the phase-in.
- Using all OPD (clinic) MA revenue divided by all OPD MA visits - for services moving to APG reimbursement (excludes mental hygiene).
Sample Blend Calculations
(for Phase One - all figures are preliminary and subject to revision)
| Region | Avg. APG Operating Payment | Avg. Existing Operating Payment | Year 1 Blend (25%/75%) | Year 2 Blend (50%/50%) | Year 3 Blend (75%/25%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Downstate | $225 | $113 | $141 | $169 | $197 |
| Upstate | $138 | $ 84 | $ 98 | $111 | $125 |
Upstate and Downstate regional base rates have been scaled to provide reimbursement equal to the same percentage of reported cost in both regions.
APG Carve-Outs and Special Payment Rules
APG Visit Carve-Outs
- All items currently carved-out of the threshold visit rate will continue to be carved-out and paid off the referred ambulatory services fee schedule - with a single exception ….
- MRIs will no longer be carved-out of the threshold visit, but instead must be billed under APGs.
- For a complete list of all APG carve-outs, including all drugs designated as chemo drugs, see carve-outs handout.
Chemo Drugs are all Carved-Out
- Chemotherapy drugs were previously carved-out of the threshold rate only for patients billed to the oncology specialty rate code 3092.
- All chemo drugs will be carved-out of APG billing for all patients. These drugs will be billable as referred ambulatory services.
- The definition of a chemo drug will be any drug that groups to one of the five chemo drug APGs.
- Some of these drug have codes that do not begin with "J9" and may have other uses besides treating cancer. Nevertheless, any drug defined under APGs as a chemo drug will be billable only off the fee schedule and will pay at zero when claimed under the APG methodology.
Billing for Drugs
- Drugs carved out of APGs will be billed against the referred ambulatory fee schedule
- For drugs in APGs:
- Class 1 Pharmacotherapy drugs will be packaged, so the costs will be included in the weight of the primary APG (significant procedure or medical visit)
- Drugs in Pharmacotherapy Classes 2 through 5 will be priced based on the Average Wholesale Prices (less 15%) of the drugs found in each group (this is consistent with the payment for drugs on the referred ambulatory fee schedule).
- A weighted average of the AWPs within each drug class will be developed based on the historical utilization of each drug. These weighted averages will then be used to set the APG relative weights for the each of the various drug APGs.
Carved-Out Injections
- Therapeutic injections continue to be carved-out as follows:
- Botulinum Toxin A
- Botulinum Toxin B
- Neupogen, Neulasta
- Aranesp (for ESRD on dialysis)
- Epogen, Procrit (for ESRD on dialysis)
Other Existing Carve-Outs Will Continue
- Blood Factors/Hemophilia
- Medical Abortion Pharmaceuticals
- Misoprostol / Mifepristone
- Family Planning Devices
- IUDs
- Contraceptive Implant (Implanon)
Lab Carve-Outs Remain Unchanged
- Laboratory Carve-Outs
- Lead screen
- HIV viral load testing
- HIV drug resistance test (Genotype, Phenotype, Virtual Phenotype)
- Hepatitis C virus, genotype test
- HIV Tropism assay
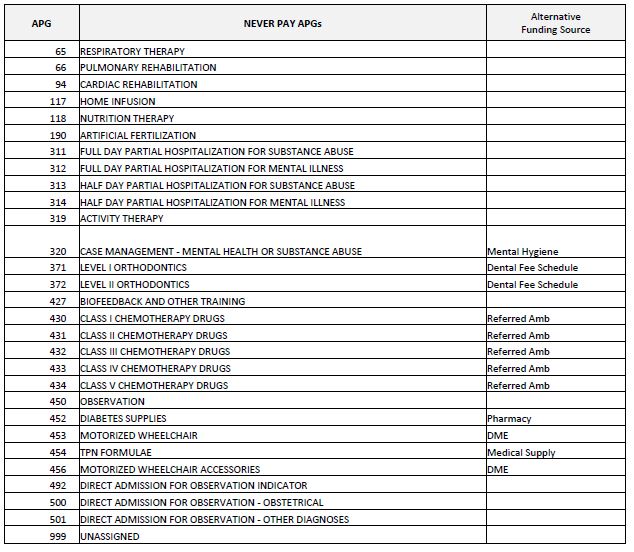
Never Pay APGs
- "Never Pay" APGs are those services that are not covered under APG reimbursement.
- Examples of Never Pay APGs include:
- Respiratory Therapy
- Cardiac Rehabilitation
- Nutrition Therapy
- Artificial Fertilization
- Biofeedback
"Never Pay" APGs (Zero Payment)
"If Stand Alone, Do Not Pay"APGs
- "Stand Alone, Do Not Pay" APGs generally consist of procedures performed as follow-up to an initial clinic visit for which APGs will not pay. These consist primarily of tests and other ancillaries.
- Mirroring the current reimbursement system, these procedures will also not pay under APGs when they are the only items claimed for a given date of service
- Examples include:
- Follow-up laboratory and diagnostic radiology testing (except MRIs) related to an initial patient encounter.
- Immunizations.
- Providers should still claim for these procedures in order to maximize the available data that can be used for future reweighting and rebasing.
Note: For those "stand alone" ancillaries that do pay (viz., MRIs), there is no capital add-on.
Claiming for "Never Pay" and "If Stand Alone Do Not Pay" APGs
- If the only items on a claim for a particular date of service (APG visit) are "Never Pays" or "If Stand Alone, Do Not Pays", then the visit will be paid at zero.
- If every item on a claim (for all dates of service), consist of these types of items, the claim will be denied. Data from these denied claims can still be used for future reweighting.
Managed Care Carve-Outs
- Rate codes that are currently used for the purpose of billing FFS Medicaid for MMC patients will remain active following the implementation of APG reimbursement.
- When MMC carved-out services are provided to a MMC recipient, these existing MMC rate codes must be used.
- When MMC carved-out services are provided to a FFS recipient, the APG rate codes must be used.
- Examples of MMC carved-out rate codes include:
- 2888 Comprehensive Physical Exam (SHP)
- 2889 Routine Visit (SHP)
Modifiers in APGs
- APGs will recognize six billing modifiers.
- 25 - distinct service
- Separately identifiable E&M service on the same day as a significant procedure (subject to DOH policy requirements)
- 27 - additional medical visit
- Separate medical visit with another practitioner on the same date of service (subject to DOH policy requirements)
- 52 - terminated procedure
- Discontinued outpatient hospital/ambulatory surgery procedure that does not require anesthesia
- 73 - terminated procedure
- Discontinued outpatient hospital/ambulatory surgery procedure, after some preparation, but prior to the administration of anesthesia
- 59 - separate procedure
- Distinct and separate multiple procedures (with same APG)
- 50 - bilateral procedure
- 25 - distinct service
Other APG Implementation Issues
PACs
- Last Updated over sixteen years ago
- All inclusive pricing
- Not reflective of new medical advances or technologies
- Ancillary pricing based upon outdated survey material
- Pricing based upon the "average visit" within a PAC group
- ICD_9 diagnosis code driven
- Visits are not weighted for intensity
- Effective December 1, 2008, PACs will be replaced by APGs (except for FQHCs - see next slide)
FQHCs and APGs
- Facility may choose to be paid under the APG methodology, or under the existing prospective payment system rate methodology
- The payment methodology selected by the FQHC would apply to all claims submitted.
- For FQHCs that switch to APG reimbursement, FQHC wraparound (shortfall) payments will continue to be paid - using the existing FQHC shortfall rate codes.
- PAC rates will continue to be available as a payment mechanism only for FQHCs that opt to continue using them instead of switching to APG payment.
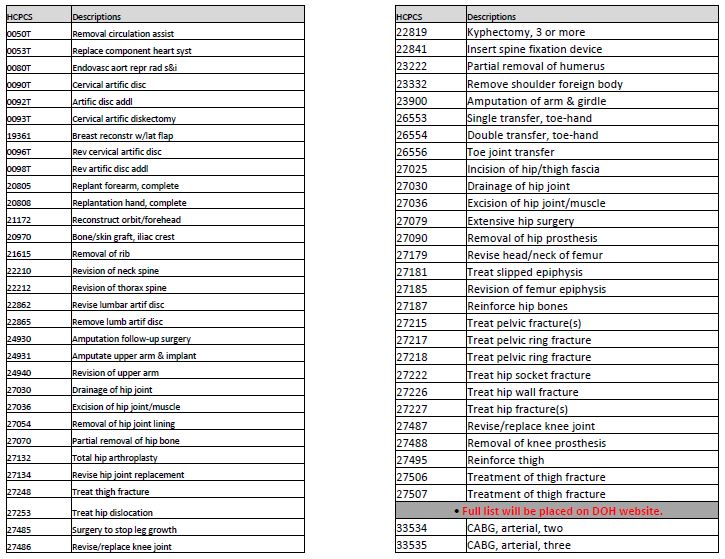
Inpatient Only
- Inpatient care will continue to be paid under DRGs.
- Certain specific surgical procedures identified within 3M the grouper / pricer (see handout) must be done on an inpatient basis only.
- These procedures may not be performed on an ambulatory surgery or on a clinic outpatient basis.
Inpatient Only List (Example - Partial List)
Ambulatory Surgery Permissible Procedures
- The ambulatory surgery base rate is higher than the OPD base rate and reflects a more intensive mode of service delivery.
- Only those visits which include a procedure designated by DOH as ambulatory surgery may be billed to the ambulatory surgery APG rate code.
- Ambulatory surgery claims may also contain non-ambulatory surgery procedures but at least one approved ambulatory surgery procedure must be claimed for each visit on the claim.
- A draft version of this list is underdevelopment and will be presented to the industry for their input.
Products of Ambulatory Surgery (Background / Issues)
- Last Updated Sixteen Years Ago
- Site Specific Basis
- All Inclusive Pricing
- Incomplete Procedure List
APG Example 3 - Ambulatory Surgery
(All procedures are grouped based on the same Date of Service)
| Gynecology/Obstetrics Visit | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPT Code | CPT Description | APG | APG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Full APG Weight | Percent Paid | Allowed APG Weight | Sample Base Rate | Paid Amount |
| 57505 | Endocervical curettage | 196 | Level I Female Reproductive Procd | Significant Procedure | Full payment | 6.4150 | 100% | 6.4150 | $186 | $1,193 |
| 87490 | Chlamydia trachomatis, direct probe technique | 394 | Level I Immunology Tests | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.1638 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 87590 | Neisseria gonorrhea, direct probe technique | 397 | Level II Microbiology Tests | Ancillary | Full payment | 0.2597 | 100% | 0.2597 | $186 | $ 48 |
| 88305 | Level IV Surgical pathology, gross and microscopic examination | 390 | Level I Pathology | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.4783 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 99215 | Office or other outpatient visit | 491 | Medical Visit Indicator | Incidental | Packaged | 1.4099 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| Operating Totals | 8.7267 | 6.6747 | $ 1,241 | |||||||
| Capital Add‐On | $ 151 | |||||||||
| Total Payment | $ 1,392 | |||||||||
Note: APG weights and base rates shown are for illustrative purposes only.
PAS verses APG Payment Example 3
- CPT 57505 Endocervical Curettage
- Pays $1,399 under APGs (from previous slide)
- Groups to PAS 31 GYN Diagnostic / Therapeutic
- All Inclusive Price
- NYC $713
- Upstate $633
APG Example 4 - Ambulatory Surgery
(All procedures are grouped based on the same Date of Service)
| Ambulatory Surgery Visit | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPT Code | CPT Description | APG | APG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Full APG Weight | Percent Paid | Allowed APG Weight | Sample Base Rate | Paid Amount |
| 31545 | Laryngoscopy, direct, operative, with operating microscope or telescope | 063 | Level II Endoscopy of Upper Air Way | Significant Procedure | Full Payment | 10.4166 | 100% | 10.4166 | $186 | $1,937 |
| 31515 | Laryngoscopy, direct, with or without tracheoscopy | 062 | Level I Endoscopy of Upper Air Way | Related Procedure | Consolidated | 2.9928 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 42405 | Salivary gland and duct Incision | 252 | Level I Facial and ENT Procedures | Unrelated Procedure | Discounted | 4.7723 | 50% | 2.3862 | $186 | $ 444 |
| 88331 | Pathology consultation during surgery, first tissue block, with frozen section, single specimen | 390 | Level I Pathology | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.4783 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 82435 | Assay of blood chloride | 402 | Basic Chemistry Tests | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.0844 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 93000 | Cardiography, electrocard., routine ECG | 413 | Cardiogram | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.2748 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 00322 | Anesth, biopsy of thyroid | 380 | Anesthesia | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.4364 | 0% | 0.0000 | $186 | $ ‐ |
| 84233 | Receptor assay estrogen | 399 | Level II Endocrinology Tests | Ancillary | Full Payment | 0.2948 | 100% | 0.2948 | $186 | $ 55 |
| Operating Totals | 19.7504 | 13.0976 | $ 2,436 | |||||||
| Capital Add‐On | $ 151 | |||||||||
| Total Payment | $ 2,587 | |||||||||
Note: APG weights and base rates shown are for illustrative purposes only.
PAS verses APG Payment Example 4
- CPT 31545 Laryngoscopy, Direct
- Pays $2,587 under APGs in NYC (previous slide)
- Groups to PAS 12 Nasal / Tracheal Endoscope
- All Inclusive Price
- NYC $682
- Upstate $600
- CPT 31515 Laryngoscopy PAS 12 $0 Payment
- CPT 42405 Biopsy of Salivary Gland PAS 9
- NYC $402 (50%)
- Upstate $355 (50%)
Medicare / Medicaid Dual Eligibles
- Medicaid will continue to pay the full annual deductible as well as the full 20% Medicare Part B coinsurance amount for all APG Medicare / Medicaid "crossover" claims.
- For FQHCs and Peer Group 41 clinics, Medicaid will continue to pay the higher of:
- the full Medicare Part B coinsurance amount,or
- the difference between the Medicare paid amount and the calculated APG payment.
Physician Billing Under APGs
- Physician services for Emergency Department and Ambulatory Surgery visits may be billed outside of APGs to the physician fee schedule.
- Physician services for OPD visits will bill based on existing payment policy.
- Physician services for DTCs are included in the APG rate (with limited exceptions).
Billing Instructions and System Issues
Provider Billing Changes
- New Rate Codes Effective 12/1/08 Dates of Service
- New APG Grouper Access Rate Codes:
- Hospital Based Outpatient Rate Code 1400
- Hospital Ambulatory Surgery Rate Code 1401
- New Rate Code Effective 1/1/09 Dates of Service
- New APG Grouper Access Rate Code:
- Hospital Emergency Room Rate Code 1402
- New APG Grouper Access Rate Code:
- Most current Rate Codes will become obsolete as of APG effective date
- See Rate Code List Handout
- For billing or adjusting dates prior to 12/1/08 use old rate code.
- Essentially, the minimum change required to bill and get paid under APGs is to code one of the new APG rate codes rather than one the existing rate codes.
- See Rate Code List Handout
- Code and Bill to Medical Record Documentation
- Complete and accurate reporting
- Procedure and diagnosis code(s)
- All services within theSAME DOSand rate code category (i.e. OPD, Amb Surg, or ED) must be billed together as one claim or only first will pay
- When 2 distinct services performed by the same provider on the same Date of Service (DOS):
- Unrelated procedure and E&M - E&M must have modifier 25 to qualify for payment
- Unrelated E&M Visits, same DOS - Second E&M must have modifier 27
- Code and Bill to Medical Record Documentation
- Complete and accurate reporting
- Procedure and diagnosis code(s)
- All services within the same DOS and rate code (based on service category - OPD, Amb Surg, ED) must be billed together on a single claim.
- If two claims are submitted, with the same rate code for the same DOS, only the first claim submitted will pay. The second will be denied.
- When 2 distinct services performed by the same provider on the same Date of Service (DOS):
- Unrelated procedure and E&M - E&M must have modifier 25 to qualify for payment.
- Unrelated E&M Visits, same DOS - Second E&M must have modifier 27 for payment.
- Bilateral Billing - Bilateral procedures are coded using modifier 50.
- To indicate the procedure was performed bilaterally submit as a single claim line using modifier 50.
- Ambulatory Surgery
- 3089 (primary procedure) and 3090 (additional procedure) become obsolete as of 12/1/08 DOS and are replaced by 1401
- Since only a single amb surg rate code, claims can no longer be split (If procedures are not combined, second APG amb surg claim will "duplicate" and deny)
- 3089 (primary procedure) and 3090 (additional procedure) become obsolete as of 12/1/08 DOS and are replaced by 1401
- Managed Care Client Carve-outs
- When services performed for managed care patient, use old/current rate codes
- APG Rate Code will deny for Prepaid Cap Recipient Service Covered By Plan (Edit 1172)
Editing Changes
- MMIS Edit 1044
- From/To Dates may not span months DOS Cannot Span Across Months
- HIPAA 835/277 Mapping
- Adjustment Reason Code 16: Claim/Service lacks information which is needed for adjudication
- Remit Remark Code N74: Resubmit with multiple claims, each claim covering services provided in only one calendar month
- Status Code 188: Statement from-through dates
- MMIS Edit 2001
- Prior payer paid amounts Claim Header and Line Payments must balance
- HIPAA 835/277 Mapping
- Adjustment Reason Code 125: Payment adjusted due to a submission/billing error(s)
- Remit Remark Code N4: Missing/incomplete/invalid prior insurance carrier EOB
- Status Code 400: Claim is out of balance
- MMIS Edit 1136
- Rate Code invalid for clinic (Do not submit add-on rate codes)
- HIPAA 835/277 Mapping
- Adjustment Reason Code 16: Claim/Service lacks information which is needed for adjudication
- Remit Remark Code M49: Missing/incomplete/invalid value code(s) or amount(s)
- Status Code: 463: NUBC value code(s) and/or amount(s)
- MMIS Edit 2081
- All APG claim lines paid zero
- Ungroupable lines
- Paid zero lines
- HIPAA 835/277 Mapping
- Adjustment Reason Code 125: Payment adjusted due to a submission/billing error(s)
- Remit Remark Code N19: Procedure incidental to primary procedure
- Status Category Code: F1: Finalized/Payment. The claim line has been paid
- Claim Status Code: 65: Claim Line Has Been Paid
Processing Changes
- "Family Planning Benefit ProgramONLY" Client Claims
- Procedures not included in FP covered list will not group to an APG nor have a price applied
- (Submit all procedures & non-FP procedures ignored)
- FP List - See Medicaid Update February 2008
- Allocating Medicare/Other Insurance
- Deductible, coinsurance, copays
- If only reported at header of claim
- Amounts from header allocated to lines
- Sum of APG payments for all lines
- Individual line payments divided by Sum of all line payments = line percentage
- Header Amounts allocated to each line by percentage
- Bundling Other Insurance Information for zero paid lines
- Reported payments, deductible, coinsurance and/or copays
- Amounts moved to line with highest adjusted weight for zero paid line
- 835 Supplemental files will contain line level detail
- Line Level processing of APG claims
- Line level COB
- Line level detail included in remittances
- 835 Changes
- Line level detail
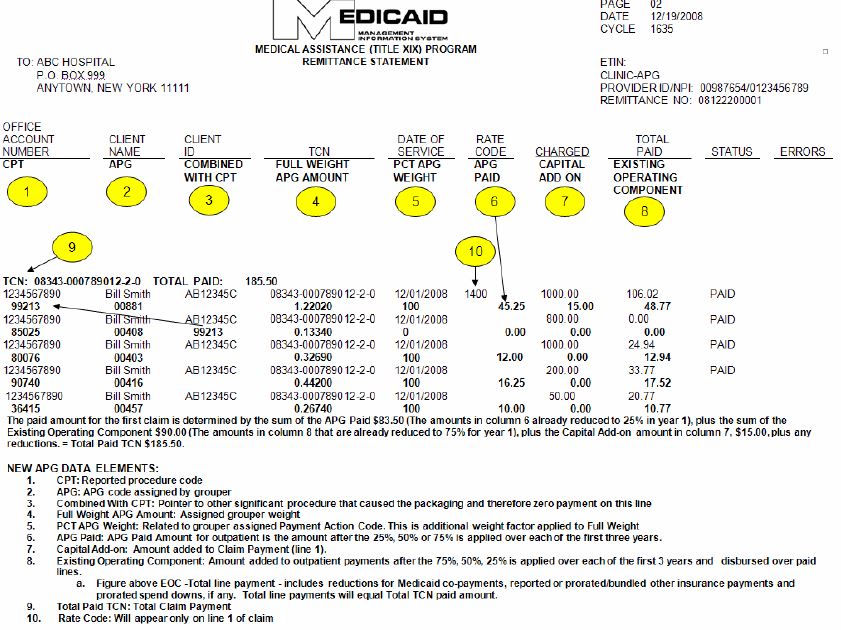
- New data elements
- Bundling
- Paper remittance example handout
- Total paid TCN above line payments
- New data elements indented for easier reading
- "Combined With CPT" links packaged CPT to significant procedure
- NPI included
- Locater Code removed
APG Example 2 – Medical Visit
(All procedures are grouped based on the same Date of Service)
| HIV/AIDS Routine Visit (Equivalent to 7 Tier ‐ Low Intensity) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPT Code | CPT Description | APG | APG Description | Payment Element | Payment Action | Full APG Weight | Percent Paid | Allowed APG Weight | Sample Base Rate | Paid Amount |
| 99213 | E & M, est. pt., low complexity (15 mins.) | 881 | AIDS | Medical Visit | Full Payment | 1.2202 | 100% | 1.2202 | $148 | $ 181 |
| 85025 | CBC w/diff | 408 | Level I Hematology Tests | Uniformly Pkgd Ancillary | Packaged | 0.1334 | 0% | 0.0000 | $148 | $ ‐ |
| 80076 | Hepatic function panel | 403 | Organ or Disease Oriented Panels | Ancillary | Full payment | 0.3269 | 100% | 0.3269 | $148 | $ 48 |
| 90740 | Hepatitis B vaccinations | 416 | Level III Immunizations | Ancillary | Full Payment | 0.4420 | 100% | 0.4420 | $148 | $ 65 |
| 36415 | Venipuncture | 457 | Venipuncture | Ancillary | Full Payment | 0.2674 | 100% | 0.2674 | $148 | $ 40 |
| Operating Totals | 2.3899 | 2.2565 | $ 334 | |||||||
| Capital Add‐On | $ 15 | |||||||||
| Total APG Payment | $ 349 | |||||||||
Note: APG weights and base rates shown are for illustrative purposes only. The primary diagnosis was AIDS (ICD-9 042). For this visit, the following carved-out services were billed to the Laboratory Fee Schedule: 87900 ($80), 87901 ($350), and 87903 ($675).
Remittance Changes (cont.)
- New 835 Remittance Data
- All new data mapped to Loop 2110
- APG Code - REF02 Qualifier 1S
- APG Full Weight - QTY02 Qualifier ZK
- APG Allowed Percentage - QTY02 Qualifier ZL
- APG Paid Amount - AMT02 Qualifier ZK
- Existing Operating Amount - AMT02 Qualifier ZK
- Combined With CPT - SVC06-2 Qualifier HC
- Line Number - REF02 Qualifier Q6
- CPT - SVC01-3 Qualifier HC
- Capital Add-on amount - CAS OA94
- Total payment for claim - CLP04
- All new data mapped to Loop 2110
Electronic Testing
- NPI Test System deployed 2nd week of September
- Available 24X7
- Test Environment will support the following transactions:
- 270/271 Eligibility
- 276/277 Claim Status
- 278 PA & Service Authorizations
- 835 Remittance Advice
- 837 Claims (Inst, Prof, Dental)
- Test Submissions
- Providers can submit up to 50 claims per test file (50 CLM Segments)
- Up to 2 test files per day
- Test files submitted and retrieved through providers´ production communication method
- Test indicator on incoming file "T" ISA15
- Test Remit delivered in providers´ production method (eXchange, iFTP, Paper or FTP)
- Test Remit Delivery
- Deliver providers´ production remit type (paper/835 + Supplemental)
- Weekly Test cycle close Fridays 2 PM
- Remits delivered weekly for sum of all test claims submitted for that week by following Monday
- Test indicator "T" ISA15
- 835 Supplemental remit file name "TEST"
- Paper remits "TEST" has watermark on each page
- No History editing
- No capability to do adjustments
- No Edits that pend a claim
- No Edits for PA and Service Auths.
Handouts & Contact Information
Supporting Materials
- Available Now
- Implementation Schedule
- APG Documentation (APG Types, APG Categories, APG Consolidation Logic)
- Payment Examples
- Uniform Packaging APGs
- Inpatient-Only Procedure List
- Never Pay and If Stand Alone Do Not Pay Lists
- Carve-Outs List
- Rate Codes List
- Remittance
- Coming Soon
- APG White Paper
- APG Policy Manual
- Running List of Frequently Asked Questions
- DOH Web Page Dedicated to APGs
- Ambulatory Surgery List
Contact Information
- Grouper/Pricer Software Support
- 3-M Health Information Systems, Inc.
- Grouper / Pricer Issues 1-800-367-2447
- Product Support 1-800-435-7776
- www.3mhis.com
- Billing Questions
- Computer Sciences Corporation
- eMedNY Call Center 1-800-343-9000
- eMedNYProviderRelations@csc.com
- Policy and Rate Issues
- New York State Department of Health
- Office of Health Insurance Programs
- Div. of Financial Planning and Policy 518-473-2160
- apg@health.state.ny.us