MRT Waiver Amendment
Behavioral Health Update
- Slides is also available in Portable Document Format (PDF)
May 2014
Greg Allen, Policy Director
Office of Health Insurance Programs
NYS Department of Health
PRESENTATION OVERVIEW
- MRT Waiver Amendment: An Overview
- MRT Waiver Amendment: State Plan Amendment (SPA)
- MRT Waiver Amendment: Managed Care
- MRT Waiver Amendment: DSRIP Program Overview
- What Has Changed in DSRIP?
- DSRIP Project Planning, Application Process & Assessment
- DSRIP Domains: Planning & Organizational Structure
- DSRIP Projects
- DSRIP Attribution
- DSRIP Project Valuation
- DSRIP Project Valuation Scenario: Illustrative Example
- DSRIP Performance Assessment
- Statewide Accountability
- DSRIP Resources
- Independent Assessor and Evaluator
- DSRIP Timeline
- MRT Waiver Amendment Stakeholder Engagement Process
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT: AN OVERVIEW
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT
- In April 2014, Governor Andrew M. Cuomo announced that New York State and CMS finalized agreement on the MRT Waiver Amendment.
- Allows the state to reinvest $8 billion of the $17.1 billion in federal savings generated by MRT reforms.
- The MRT Waiver Amendment will:
- ✓ Transform the state´s Health Care System
- ✓ Bend the Medicaid Cost Curve
- ✓ Assure Access to Quality Care for all Medicaid members
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT: $8 BILLION ALLOCATION
- $500 Million for the Interim Access Assurance Fund (IAAF) – Time limited funding to ensure current trusted and viable Medicaid safety net providers can fully participate in the DSRIP transformation without unproductive disruption.
- $6.42 Billion for Delivery System Reform Incentive Payments (DSRIP) – Including DSRIP Planning Grants, DSRIP Provider Incentive Payments, and DSRIP Administrative costs and DSRIP related Workforce Transformation.
- $1.08 Billion for other Medicaid Redesign purposes – This funding will support Health Home development, and investments in long term care workforce and enhanced behavioral health services, (1915i services).
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT HAS SIGNIFICANT FOCUS ON BEHAVIORAL HEALTH
- Waiver Amendment includes $645.9 Million for enhanced behavioral health services
- DSRIP funds will flow to managed care plans who will be required to contract for the 1915i services
- State to develop a targeted pilot for assessment, network development, and person–centered planning for community based services
- New York´s´ MLTSS transition for individuals with SMI /SUD represents a major system transformation consistent with the goals of Olmstead
OTHER KEY INITIATIVES
- Other key initiatives that support MRT Waiver Amendment implementation in New York:
- ✓ $1.2 billion in capital investment enacted in 2014–15 budget.
- ✓ Regulatory relief to support provider collaboration on DSRIP projects.
- ✓ More information to follow.
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT
- Stayed true to the original goals of the MRT Waiver Amendment (August 2012), while making our proposal consistent with CMS feedback on what could be approved.
- While the overall concept is the same, there are a number of structural changes that have been negotiated. These include:
- ✓ Funding Levels
- ✓ Safety Net Definition (for DSRIP)
- ✓ Program Components
- ✓ Timeline
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT KEY DOCUMENTS
MRT Waiver Amendment – official governing documents:
- Partnership Plan Special Terms and Conditions (STCs)
- ✓ Governing agreement between New York and CMS of Partnership Plan 1115 Waiver. MRT Waiver Amendment STCs outline implementation of MRT Waiver Amendment programs, authorized funding sources and uses, and other requirements
- Attachment I: Program Funding and Mechanics Protocol
- ✓ Describes the state and CMS process for reviewing DSRIP project plans, incentive payment methodologies, reporting requirements, and penalties for missed milestones
- Attachment J: Strategies and Metrics Menu
- ✓ Describes strategies and metrics available to Performing Provider Systems for including in their DSRIP Project Plan
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT: STATE PLAN AMENDMENT (SPA)
STATE PLAN AMENDMENT (SPA) KEY CONCEPTS
- Health Home Development Funds would support programs, including:
- ✓ Member Engagement and Health Home Promotion;
- ✓ Workforce Training and Retraining;
- ✓ Clinical Connectivity – HIT Implementation; and
- ✓ Joint Governance Technical Assistance and Implementation Funds.
- Health Home Development Funds will be distributed through a CMS approved rate add–on.
- Total 5–year value = $190.6 million.
- More information to follow.
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT: MANAGED CARE
MANAGED CARE CONTRACT AMENDMENTS
- Vehicle to implementing:
- Long Term Care Workforce Strategy ($245.0mm)
- 1915i Services ($645.9mm)
- Funds will flow to plans who will be required to contract for those services.
- Plans for how funds will be used will be pre–approved by the state.
- Total five*#8211'year value = $890.9 million.
- More information to follow.
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT: DELIVERY SYSTEM REFORM INCENTIVE PAYMENT (DSRIP) PROGRAM OVERVIEW
DSRIP KEY GOALS REMAIN:
- Transformation of the health care safety net at both the system and state level.
- Reducing avoidable hospital use and improve other health and public health measures at both the system and state level.
- Ensure delivery system transformation continues beyond the waiver period through leveraging managed care payment reform.
- Near term financial support for vital safety net providers at immediate risk of closure.
INTERIM ACCESS ASSURANCE FUND: SHORT TERM FINANCIAL SUPPORT
- Interim Access Assurance Fund (IAAF) is temporary, time limited funding to protect against degradation of the current key health care services until DSRIP is implemented.
- Total IAAF allocation is $500 million ($250 million for public hospitals, $250 million for non–public hospitals).
- The state will make all decisions regarding eligibility and distribution, however, will be limited to providers serving significant numbers of Medicaid members who are at high financial risk.
- Awardees must be part of a submitted DSRIP application.
- More information to follow.
NYS DSRIP PLAN: KEY COMPONENTS
- Key focus on reducing avoidable hospitalizations by 25% over five years.
- Statewide initiative open to large public hospital systems and a wide array of safety–net providers.
- Payments are based on performance on process and outcome milestones.
- Providers must develop projects based upon a selection of CMS approved projects from each of three domains.
- Key theme is collaboration! Communities of eligible providers will be required to work together to develop DSRIP project proposals.
DSRIP PROGRAM PRINCIPLES REMAIN
| Patient–Centered |
|
| Transparent |
|
| Collaborative |
|
| Accountable |
|
| Value Driven |
|
| Better care, less cost | |
PERFORMING PROVIDER SYSTEMS (PPS):
LOCAL PARTNERSHIPS TO TRANSFORM THE DELIVERY SYSTEM
Partners should include:
- Hospitals
- Health Homes
- Skilled Nursing Facilities
- Clinics & FQHCs
- Behavioral Health Providers
- Home Care Agencies
- Other Key Stakeholders
Responsibilities must include:
- Community health care needs assessment based on multi–stakeholder input and objective data.
- Building and implementing a DSRIP Project Plan based upon the needs assessment in alignment with DSRIP strategies.
- Meeting and reporting on DSRIP Project Plan process and outcome milestones.
WHAT HAS CHANGED IN DSRIP?
Safety Net Definition
Further Specifications of Key Components
DSRIP Timeline
SAFETY NET DEFINITION (HOSPITALS)
- A hospital must meet one of the three following criteria to participate in a performing provider system:
- Must be either a public hospital, Critical Access Hospital or Sole Community Hospital,
OR ... - Must pass two tests:
- At least 35 percent of all patient volume in their outpatient lines of business must be associated with Medicaid, uninsured and Dual Eligible individuals.
- At least 30 percent of inpatient treatment must be associated with Medicaid, uninsured and Dual Eligible individuals;OR ...
- Must serve at least 30 percent of all Medicaid, uninsured and Dual Eligible members in the proposed county or multi–county community. The state will use Medicaid claims and encounter data as well as other sources to verify this claim. The state reserves the right to increase this percentage on a case by case basis so as to ensure that the needs of each community´s Medicaid members are met.
- Must be either a public hospital, Critical Access Hospital or Sole Community Hospital,
SAFETY NET DEFINITION (NON–HOSPITAL BASED PROVIDERS & NON–QUALIFYING DSRIP PROVIDERS)
- Non–hospital based providers, not participating as part of a state– designated Health Home, must have at least 35 percent of all patient volume in their primary lines of business associated with Medicaid, uninsured and Dual Eligible individuals.
- Non–qualifying providers, can participate in Performing Providers Systems. However, no more than 5 percent of a project´s total valuation may be paid to non–qualifying providers. This 5 percent limit applies to non–qualifying providers as a group. CMS can approve payments above this amount if it is deemed in the best interest of Medicaid members attributed to the Performing Provider System.
SAFETY NET DEFINITION
(VITAL ACCESS PROVIDER EXCEPTION)
Vital Access Provider Exception: The state will consider exceptions to the safety net definition on a case–by–case basis if it is deemed in the best interest of Medicaid members. Any exceptions that are considered must be approved by CMS and must be posted for public comment 30 days prior to application approval. Three allowed reasons for granting an exception are:
- ✓ A community will not be served without granting the exception because no other eligible provider is willing or capable of serving the community.
- ✓ Any hospital is uniquely qualified to serve based on services provided, financial viability, relationships within the community, and/or clear track record of success in reducing avoidable hospital use.
- ✓ Any state–designated Health Home or group of Health Homes.
DSRIP TERMINOLOGY
- Providers that form partnerships and collaborate in a DSRIP Project Plan are now referred to as a Performing Provider System (PPS).
- The DSRIP program contains four evaluation Domains. Domains 2 and 3 are further broken into specific strategy areas. Under each strategy are a number of projects.
Performing Provider System
- Domains
↘- Strategies
↘- Projects
↘- DSRIP Project Plan
- Projects
- Strategies
UPDATED DSRIP PROJECT TIMELINE

DSRIP PROJECT PLANNING, APPLICATION PROCESS & ASSESSMENT (YEAR 0)
DSRIP PROJECT PLAN REQUIREMENTS
The project must be:
- A new initiative for the Performing Provider System (PPS);
- Substantially different from other initiatives funded by CMS, although it may build on or augment such an initiative;
- Documented to address one or more significant issues within the PPS service area and be based on a detailed analysis using objective data sources;
- A substantial, transformative change for the PPS;
- Demonstrative of a commitment to life–cycle change and a willingness to commit sufficient organizational resources to ensuring project success;
- Developed, in concert, with other providers in the service area with special attention paid to coordination with Health Homes actively working within their area; and
- Applications from single providers will not be considered!
DSRIP PROJECT DESIGN GRANT REVIEW AND APPROVAL PROCESS
| 1. Provider Submits Project Design Grant Application |
|
| 2. State Reviews Project Design Grant Application |
|
| 3. Provider submits Progress Report to DOH |
|
| 4. Provider submits a DSRIP Project Plan to DOH (Dec 2014) |
|
| 5. Final Notification |
|
DSRIP DOMAINS: PLANNING & ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE
DSRIP DOMAINS
- Project implementation is divided into four Domains for project selection and reporting:
- Domain 1 – Overall Project Progress
- Domain 2 – System Transformation
- Domain 3 – Clinical Improvement
- Domain 4 – Population–wide Strategy Implementation – The Prevention Agenda
Through innovations in these four domains, the statewide DSRIP plan is designed to reduce avoidable hospitalizations by 25% over five years.
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT DOMAINS HAS A FOCUS ON BEHAVIORAL HEALTH
- Domain 2 (System Transformation) projects that have behavioral health options
- Domain 3 (Clinical Improvement) requirements requires all applicants carry out a Behavioral Health project
- Domain 4 (Population–wide Projects) has behavioral health options.
- DSRIP High Performing Fund includes incentive payments specifically for reductions of behavioral health hospitalizations.
DSRIP DOMAINS
Domain 1: Overall Project Progress
- Investments in technology, tools, and human resources that will strengthen the ability of the Performing Providers Systems (PPS) to serve target populations and pursue DSRIP project goals.
- Performing Providers Systems (PPS) will need to submit a detailed project plan for implementation of their chosen project.
- Performance in this domain will be measured on meeting identified milestones in the project plan and progress to sustainability.
Domain 2: System Transformation
- Projects in this domain focus on system transformation and fall into three strategy sublists:
- Create integrated delivery system
- Implementation of care coordination and transitional care programs
- Connecting system
- All PPS must select at least two projects (and up to four projects) from Domain 2:
- ✓ At least one project must be from strategy sublist A (see attachment J)
- ✓ At least one project must be from strategy sublist B or C (see attachment J)
- Metrics will include avoidable hospitalizations and other measures of system transformation. DS
Domain 3: Clinical Improvement
- Projects in this domain focus on clinical improvement for certain priority disease categories.
- All PPS must select at least two (but no more than four) projects from Domain 3:
- ✓ At least one project must be from strategy sublist A (behavioral health)
- Metrics will include disease focused nationally recognized and validated metrics, generally from HEDIS.
Domain 4: Population–wide Strategy Implementation
- Projects in this domain are aligned to the NYS Prevention Agenda and should align with projects in Domain 3.
- Performing Provider Systems will select one (but no more than two) projects from at least one of the four priority areas:
✓ Promote Mental Health and Prevent Substance Abuse;
✓ Prevent Chronic Disease;
✓ Prevent HIV/AIDS; and
✓ Promote Health Women, Infants and Children. - Reporting will be on progress PPS have made in implementing the aligned strategies.
- Link to the New York State Prevention Agenda.
|top of section| |top of page|
DSRIP PROJECTS
DSRIP PROJECTS
- Safety net providers must choose a specified number of projects from Domains 2, 3 and 4.
- Each project has the following components specifically tied to the goal of reducing avoidable hospitalizations:
- ✓ Clearly defined process measures;
- ✓ Clearly defined outcome measures;
- ✓ Clearly defined measures of success relevant to provider type and population impacted; and
- ✓ Clearly defined financial sustainability metrics to assess long–term viability.
DOMAIN 2: SYSTEM TRANSFORMATION STRATEGY AREAS: INTEGRATED DELIVERY SYSTEMS / CARE COORDINATION & TRANSITIONAL CARE PROGRAMS / CONNECTING SETTINGS
*Index Score: An evaluation or score assigned to DSRIP projects, based on five elements (1. Potential for achieving system transformation, 2. Potential for reducing preventable event, 3. % of Medicaid beneficiaries affected by project, 4. Potential Cost Savings and 5. Robustness of Evidence Based suggestions). Project index scores are set by the state and are released prior to the application period.
^Bolded project numbers with the carrot notation: indicates that the project contains a behavioral health component.
A. Create Integrated Delivery Systems (Required)
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.a.i^ | Create Integrated Delivery Systems that are focused on Evidence Based Medicine / Population Health Management | 56 |
| 2.a.ii^ | Increase certification of primary care practitioners with PCMH certification and/or Advanced Primary Care Models (as developed under the New York State Health Innovation Plan [SHIP]) | 37 |
| 2.a.iii^ | Health Home At Risk Intervention Program– Proactive management of higher risk patients not currently eligible for Health Homes through access to high quality primary care and support services. | 46 |
| 2.a.iv | Create a medical village using existing hospital infrastructure. | 54 |
| 2.a.v | Create a medical village/ alternative housing using existing nursing home. | 42 |
B. Implementation of care coordination and transitional care programs
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.b.i^ | Ambulatory ICUs | 36 |
| 2.b.ii | Development of co–located of primary care services in the emergency department (ED) | 40 |
| 2.b.iii | ED care triage for at–risk populations | 43 |
| 2.b.iv | Care transitions intervention model to reduce 30 day readmissions for chronic health conditions | 43 |
| 2.b.v | Care transitions intervention for skilled nursing facility residents | 41 |
| 2.b.vi^ | Transitional supportive housing services | 47 |
| 2.b.vii | Implementing the INTERACT project (inpatient transfer avoidance program for SNF) | 41 |
| 2.b.viii | Hospital–Home Care Collaboration Solutions | 45 |
| 2.b.ix^ | Implementation of observational programs in hospitals | 36 |
C. Connecting Settings
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 2.c.i | Development of community–based health navigation services | 37 |
| 2.c.ii^ | Expand usage of telemedicine in underserved areas to provide access to otherwise scarce services | 31 |
DOMAIN 3: CLINICAL IMPROVEMENT PROJECTS STRATEGY AREAS: BEHAVIORAL HEALTH / CARDIOVASCULAR HEALTH / DIABETES CARE / ASTHMA / HIV / PERINATAL / PALLIATIVE / RENAL
A. Behavioral health (required)
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.a.i^ | Integration of primary care services and behavioral health | 39 |
| 3.a.ii^ | Behavioral health community crisis stabilization services | 37 |
| 3. a.iii^ | Implementation of evidence based medication adherence program (MAP) in community based sites for behavioral health medication compliance. | 29 |
| 3.a.iv^ | Development of withdrawal management (ambulatory detoxification) capabilities within communities. | 36 |
| 3.a.v^ | Behavioral Interventions Paradigm in Nursing Homes (BIPNH). | 40 |
B. Cardiovascular Health
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.b.i | Evidence based strategies for disease management in high risk/affected populations (adult only) | 30 |
| 3.b.ii | Implementation of evidence–based strategies in the community to address chronic disease –– primary and secondary prevention projects (adult only) | 26 |
(PPS should utilize strategies contained in the Million Hearts campaign as appropriate.)
C. Diabetes Care
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.c.i | Evidence–based strategies for disease management in high risk/affected populations (adults only) | 30 |
| 3.c.ii | Implementation of evidence–based strategies in the community to address chronic disease – primary and secondary prevention projects (adults only) | 26 |
D. Asthma
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.d.i | Development of evidence–based medication adherence programs (MAP) in community settings –asthma medication | 28 |
| 3.d.ii | Expansion of asthma home–based self– management program | 31 |
| 3.d.iii | Evidence based medicine guidelines for asthma management | 31 |
E. HIV
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 3.e.i | Comprehensive Strategy to decrease HIV/AIDS transmission to reduce avoidable hospitalizations – development of a Center of Excellence for management of HIV/AIDS. | 28 |
F. Perinatal
| Project # | Description | Index Score |
|---|---|---|
| 3.f.i | Increase support programs for maternal & child health (including high risk pregnancies) (Example: Nurse–Family Partnership) | 29 |
G. Palliative
| Project # | Description | Index Score |
|---|---|---|
| 3.g.i | IHI "Conversation Ready" model | 29 |
| 3.g.ii | Integration of palliative care into medical homes | 22 |
| 3.g.iii | Integration of palliative care into nursing homes | 25 |
H. Renal
| Project # | Description | Index Score |
|---|---|---|
| 3.h.i | Specialized Medical Home from Chronic Renal Failure | 29 |
DOMAIN 4: POPULATION–WIDE PROJECTS STRATEGY AREAS: MH & SUD/CHRONIC DISEASE/ HIV & STDS / WIC
The following represent priorities from the State´s Prevention Agenda. At least one project from this domain must be chosen, based upon the community assessment:
A. Promote Mental Health and Prevent Substance Abuse
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 4.a.i.^ | Promote mental, emotional and behavioral (MEB) well–being in communities | 23 |
| 4.a.ii.^ | Prevent Substance Abuse and other Mental Emotional Behavioral Disorders | 20 |
| 4.a.iii.^ | Strengthen Mental Health and Substance Abuse Infrastructure across Systems | 20 |
B. Prevent Chronic Diseases
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 4.b.i. | Promote tobacco use cessation, especially among low SES populations and those with poor mental health. | 23 |
| 4.b.ii. | Increase Access to High Quality Chronic Disease Preventive Care and Management in Both Clinical and Community Settings. | 17 |
C. Prevent HIV and STDs
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 4.c.i | Decrease HIV morbidity; | 19 |
| 4.c.ii | Increase early access to, and retention in, HIV care; | 19 |
| 4.c.iii | Decrease STD morbidity; and | 15 |
| 4.c.iv | Decrease HIV and STD Disparities | 18 |
D. Promote Healthy Women, Infants and Children
| Project # | Description | Index Score* (out of 60 pts) |
|---|---|---|
| 4.d.i | Reduce Premature Births | 24 |
DSRIP PERFORMANCE MEASURES: DOMAIN 2
AVOIDABLE HOSPITALIZATIONS
The following four measures will be used to evaluate DSRIP´s success in reducing avoidable hospital use:
- ✓ Potentially Preventable Emergency Room Visits (PPVs).
- ✓ Potentially Preventable Readmissions (PPRs).
- ✓ Prevention Quality Indicators– Adult (PQIs).
- ✓ Prevention Quality Indicators– Pediatric (PDIs),
SYSTEM TRANSFORMATION
Other measures will be used to monitor system transformation and fiscal stability:
- ✓ % Alternate payment strategies in Medicaid
- ✓ System Integration measures
- ✓ PCMH Attainment
- ✓ Access to care measures
- ✓ Care transitions measures
DSRIP PERFORMANCE MEASURES: DOMAIN 3 – CLINICAL IMPROVEMENT
Each Domain 3 strategy has assigned metrics specific to the strategy subject.
For example, for A. Behavioral Health, these include:
- ✓ Antidepressant Medication Management.
- ✓ Follow–up after hospitalization for Mental Illness (NCQA).
- ✓ Cardiovascular monitoring for People with CVD and Schizophrenia.
Note: Metrics are chosen from nationally recognized, validated measures.
DSRIP PERFORMANCE MEASURES: DOMAIN 4 – POPULATION WIDE
Domain 4 measures are those already measured by the state in the Prevention Agenda and include the total population for the PPS area (not just Medicaid Members). As examples:
- ✓ Percentage of adults who are obese
- ✓ Age–adjusted heart attack hospitalization rate per 10,000
- ✓ Percentage of premature death (before age 65)
- Ratio of Black non–Hispanics to White non–Hispanics
- Ratio of Hispanics to White non–Hispanics
|top of section| |top of page|
DSRIP ATTRIBUTION
DSRIP ATTRIBUTION: MATCHING MEMBERS TO A PPS
- Attribution is the process used in DSRIP to assign a member to a Performing Provider System (PPS).
- Attribution makes sure that each Medicaid member is assigned to one and only one PPS.
- Attribution uses geography, patient visit information and health plan PCP assignment to "attribute" a member to a given PPS.
- Patient visit information is used to establish a "loyalty" pattern to a PPS (based on all their provider members) where most of the member´s services are rendered.
DSRIP ATTRIBUTION: SOLE PPS IN GEOGRAPHICAL REGION
When there is only one Performing Provider System (PPS) in a defined geographic area/geopolitical area, the entire matched Medicaid beneficiary population will be the assigned population in that geographic/geopolitical area.
DSRIP ATTRIBUTION: MULTIPLE PPS IN GEOGRAPHICAL REGION
When there is more than one Performing Provider System in a defined geographic/geopolitical area, the following methodology will be utilized*:
- Matching Goal – Assignment to a PPS based on the recipient´s current utilization patterns, including plurality of visits. Beneficiaries who receive plurality of their qualifying services from providers that are not participating in any DSRIP Performing Provider System will be excluded from attribution.
- Service Groupings – To meet this goal, the methodology will aggregate patient service volume across four different groups of services and assign attribution using a hierarchical service priority as follows:
- ✓ 1st priority – care management provider;
- ✓ 2nd priority – outpatient (physical and behavioral health) including Primary Care Providers and other practitioners;
- ✓ 3rd priority – emergency room; and
- ✓ 4th priority – inpatient.
- Attribution Method – Once the PPS network of service providers is finalized that overall PPS´ service network will be loaded into the attribution system for recipient loyalty to be assigned based on total visit counts to the overall PPS network in each of the hierarchical service categories (mentioned in the last side).
- Attribution Adjustments/MCO Input – Adjustments to attribution based on known variables (e.g., recent changes to the recipient´s address, PCP assignment, recent changes in access patterns) may be made by the state with MCO input if deemed appropriate by data. A methodology is also employed to assign unmatched members. At the end of each measurement year adjustments may be made for the purpose of denominator development.
- Final Attribution Assignment – After all visits against all providers are tallied up for a given service type and appropriate adjustments made, the methodology assigns the member to a single PPS.
- Attribution For Measurement – At the end of each measurement period, attribution will be adjusted to account for continuous enrollment criteria and any other adjustments necessary to assure a proper measurement denominator.
* A methodology for including long term care services and supports will need to be developed. Priority may also be modified based on PCP assignment and utilization.
* More information to follow
|top of section| |top of page|DSRIP PROJECT VALUATION
The maximum DSRIP project and application valuation will follow a five–step process.
STEP 1: PROJECT INDEX SCORE
- Each project in the DSRIP Strategy Menu (Attachment J) is given a Project Index Score which is a ratio out of a total of 60 possible points of each project (X/60 = project index score).
- Project Index Scores are based upon a grading rubric that evaluated the project´s ability to transform the health care system. The State has assigned an index score to each project based on the grading rubric.
Five elements
(Total: 60pt max per project)
- Potential for achieving system transformation.............30pts
- Potential for reducing preventable event........................10pts
- Capacity for Project to affect Medicaid beneficiaries....10pts
- Potential Cost Savings to Medicaid...................................5pts
- Robustness of Evidence Based suggestion...................5pts
Step 1a: Index Score (IS)
- Projects are evaluated across 5 elements and given an index score.
- Individual project index scores are set by DOH and are released prior to the application period
Step 1b: Convert Index Score into a Project Index Score
The IS is then divided by the maximum index score (MIS) to get the Project Index Score (PIS) [IS] / [MIS] = PIS
STEP 2: PROJECT PMPM
- The second step creates a project PMPM (per member per month) by multiplying the project index score by the state´s valuation benchmark.
- The valuation benchmark is pre–set by the state and varies based upon the number of projects proposed by an applicant.
- Since additional projects will share infrastructure and resources, the valuation benchmark is discounted as applicants select additional projects.
- Although the project PMPM levels drop with the inclusion of additional projects, the overall Performing Project System valuation will generally increase as more projects are added to the overall PPS effort.
Project PMPM
Step 2a: Valuation Benchmark
Valuation benchmark will be an assigned value, derived from similar delivery reforms, expressed in a PMPM format and will be provided by DOH based upon the number of project an applicant selects.
Step 2b: Project PMPM
[project index score] × [valuation benchmark] = Project PMPM
STEP 3: PLAN APPLICATION SCORE
- The third step determines the plan application score based on a total of 100 points possible for each application (X/100 = Application Score).
- Score will drive the percent of the maximum project valuation for each project.
- Score based on the fidelity to the project description, and likelihood of achieving improvement by using that project.
- The state is developing a grading system for the plan application score in collaboration with CMS. This grading system will ensure non–duplication of projects/efforts within a project plan.
- Applications are scored by independent assessor and makes recommendations.
- Performing provider systems are encouraged to partner with providers participating in the IAAF program as part of their DSRIP performance network. The plan application score rubric developed by state in collaboration with CMS may include bonus points for addressing sustainability issues in communities served by IAAF providers.
- Applications will also be scored based on an applicant´s commitment to developing a capability to responsibly receive risk–based payments from managed care plans through the DSRIP project period.
STEP 4: MAXIMUM PROJECT VALUE
In the fourth step, the Maximum Project Value is calculated by multiplying:
- ✓ the project PMPM,
- ✓ the project plan application score,
- ✓ the number of Medicaid beneficiaries attributed to the project,
- ✓ and the duration of the DSRIP project.
Maximum Project Value = [Project PMPM] × [# of Medicaid Beneficiaries] × [Plan Application Score] × [DSRIP Project Duration]
Maximum Project Valuation Notes
Note on Member Attribution:
Applicants will provide an attribution assessment in their submission (to be verified by the assessor) identifying the number of Medicaid beneficiaries that are intended to benefit from their project.
Note on Project Duration:
The DSRIP Program Duration is set to be 60 months. The application valuation will assume that providers are to participate in the program for the entire time.
Maximum Project Value =
[Application PMPM] × [Project Plan Application Score] × [# of Medicaid beneficiaries] × [Duration of DSRIP Program]
STEP 5: MAXIMUM APPLICATION VALUE
- Once the maximum project values have been determined, the maximum application value for a Performing Provider System is calculated by adding together each of the maximum project values for a given Performing Provider System´s application.
- The maximum application value represents the highest possible financial allocation a Performing Provider System can receive for their project plan over the duration of their participation in the DSRIP program.
- Performing Provider Systems may receive less than their maximum allocation if they do not meet metrics and/or if DSRIP funding is reduced because of the statewide penalty).
DSRIP PROJECT VALUATION SCENARIO: ILLUSTRATIVE EXAMPLE
DSRIP SCENARIO: HPI* PROJECT VALUATION
STEP 1: PROJECT INDEX SCORES
| HPI Project Plan (containing 6 projects) | Project Index Scores |
|---|---|
| Project 1: 2.a.i Create Integrated Delivery Systems that are focused on EBM/PHM to reduce avoidable hospitalizations | 0.93 |
| Project 2: 2.a.ii Increase certification of primary care practitioners with PCMH certification to reduce avoidable hospitalizations | 0.62 |
| Project 3: 2.b.vii Implementing the INTERACT project (inpatient transfer avoidance program for Skilled Nursing Facility) | 0.68 |
| Project 4: 3.a.i Integration of primary care and behavioral health services(Behavioral Health) | 0.65 |
| Project 5: 3.c.i Evidenced based strategies for disease management in high risk populations (Cardiovascular Health) | 0.48 |
| Project 6: Domain 4 Focus Area B. Reduce illness, disability and death related to tobacco use and secondhand smoke exposure | 0.38 |
* HPI is "Health Partners Initiative" – a fictitious performing provider system – for illustration purposes.
DSRIP SCENARIO: PROJECT VALUATION
VALUATIONBENCHMARK TABLE
Below is the current state valuation benchmark table with a benchmark baseline of $8.
| Number of projects | Valuation Benchmark PMPMs* |
|---|---|
| 5 (minimum allowed) | $8.00 |
| 6 | $7.20 |
| 7 | $6.80 |
| 8 | $6.65 |
| 9 | $6.50 |
| 10 (maximum allowed) | $6.50 |
* PMPMs drop as more projects are added to account for the ability to leverage shared capacities (e.g., administration, IT systems etc.).
DSRIP SCENARIO: HPI PROJECT VALUATION
STEP 2: PROJECT PMPM
| HPI Project Plan (containing 6 projects) | Project Index Scores | Valuation Benchmark (5 Project Base Value =$8) |
Project PMPM |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project 1: 2.a.i Create Integrated Delivery Systems that are focused on EBM/PHM to reduce avoidable hospitalizations | 0.93 | $7.20 | $6.70 |
| Project 2: 2.a.ii Increase certification of primary care practitioners with PCMH certification to reduce avoidable hospitalizations | 0.62 | $7.20 | $4.46 |
| Project 3: 2.b.vii Implementing the INTERACT project (inpatient transfer avoidance program for Skilled Nursing Facility) | 0.68 | $7.20 | $4.90 |
| Project 4: 3.a.i Integration of primary care and behavioral health services(Behavioral Health) | 0.65 | $7.20 | $4.68 |
| Project 5: 3.c.i Evidenced based strategies for disease management in high risk populations (Cardiovascular Health) | 0.48 | $7.20 | $3.46 |
| Project 6: Domain 4 Focus Area B. Reduce illness, disability and death related to tobacco use and secondhand smoke exposure | 0.38 | $7.20 | $2.74 |
DSRIP SCENARIO: HPI PROJECT VALUATION
STEP 3: PROJECT PLAN APPLICATION SCORE STEP
4: MAXIMUM PROJECT VALUATION
| HPI Project Plan (containing 6 projects) | Project PMPM | Project Plan Application Score | # of Attributed Medicaid Members | # of DSRIP Months | Maximum Project Valuation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project 1: 2.a.i Create Integrated Delivery Systems that are focused on EBM/PHM to reduce avoidable hospitalizations | $6.70 | 0.85 | 10,000 | 60 | $3,417,000 |
| Project 2: 2.a.ii Increase certification of primary care practitioners with PCMH certification to reduce avoidable hospitalizations | $4.46 | 0.85 | 10,000 | 60 | $2,274,600 |
| Project 3: 2.b.vii Implementing the INTERACT project (inpatient transfer avoidance program for Skilled Nursing Facility) | $4.90 | 0.85 | 10,000 | 60 | $2,499,000 |
| Project 4: 3.a.i Integration of primary care and behavioral health services(Behavioral Health) | $4.68 | 0.85 | 10,000 | 60 | $2,386,800 |
| Project 5: 3.c.i Evidenced based strategies for disease management in high risk populations (Cardiovascular Health) | $3.46 | 0.85 | 10,000 | 60 | $1,764,600 |
| Project 6: Domain 4 Focus Area B. Reduce illness, disability and death related to tobacco use and secondhand smoke exposure | $2.74 | 0.85 | 10,000 | 60 | $1,397,400 |
DSRIP SCENARIO: HPI PROJECT VALUATION
STEP 5: MAXIMUM APPLICATION VALUE
| HPI Project Plan (Containing 6 projects) | Maximum Project Valuation |
|---|---|
| Project 1: 2.a.i Create Integrated Delivery Systems that are focused on EBM/PHM to reduce avoidable hospitalizations | $3,417,000 |
| Project 2: 2.a.ii Increase certification of primary care practitioners with PCMH certification to reduce avoidable hospitalizations | $2,274,600 |
| Project 3: 2.b.vii Implementing the INTERACT project (inpatient transfer avoidance program for Skilled Nursing Facility) | $2,499,000 |
| Project 4: 3.a.i Integration of primary care and behavioral health services(Behavioral Health) | $2,386,800 |
| Project 5: 3.c.i Evidenced based strategies for disease management in high risk populations (Cardiovascular Health) | $1,764,600 |
| Project 6: Domain 4 Focus Area B. Reduce illness, disability and death related to tobacco use and secondhand smoke exposure | $1,397,400 |
| Maximum Application Value | $13,739,400* |
*The maximum application value represents the highest possible financial allocation a Performing Provider System can receive for their project plan over the duration of their participation in the DSRIP program.
Performing Provider Systems may receive less than their maximum allocation if they do not meet metrics and/or if DSRIP funding is reduced because of the statewide penalty).
|top of section| |top of page|DSRIP PERFORMANCE ASSESSMENT
All DSRIP Payments Linked to Performance
DSRIP FINANCE FRAMEWORK
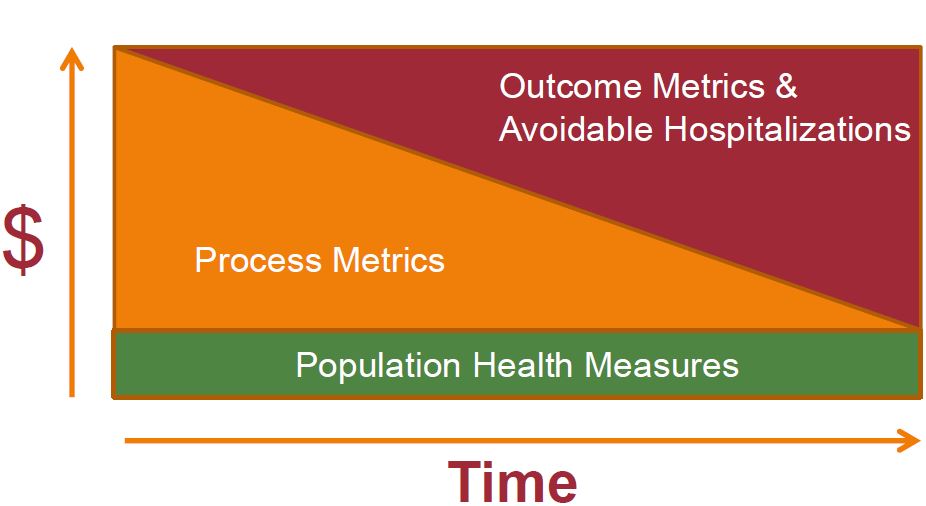
DSRIP FUNDING DISTRIBUTION STAGES
- DSRIP payments for each provider are contingent on them meeting program and project metrics and milestones defined in the DSRIP Plan and consistent with the valuation process.
- Based upon a project´s valuation, incentive payment values will be calculated for each metric/milestone domain in the DSRIP project plan by multiplying the total valuation of the project in a given year by the milestone percentages specified below.
| Metric/Milestone Domains | Performance Payment* | Year 1 (CY 15) |
Year 2 (CY 16) |
Year 3 (CY 17) |
Year 4 (CY 18) |
Year 5 (CY 19) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Project progress milestones (Domain 1) | P4R/ P4P | 80% | 60% | 40% | 20% | 0% |
| System Transformation and Financial Stability Milestones (Domain 2) | P4P | 0% | 0% | 20% | 35% | 50% |
| P4R | 10% | 10% | 5% | 5% | 5% | |
| Clinical Improvement Milestones (Domain 3) | P4P | 0% | 15% | 25% | 30% | 35% |
| P4R | 5% | 10% | 5% | 5% | 5% | |
| Population health Outcome Milestones (Domain 4) | P4R | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% | 5% |
P4R = Pay for Reporting
P4P = Pay for Performance
DSRIP PERFORMANCE MILESTONES – PAY FOR PERFORMANCE
- Annual improvement targets with use a methodology of reducing the gap to the goal by 10%.
- For example, if the baseline data for a measure is 52 percent and the goal is 90 percent, the gap to the goal is 38. The target for the project´s first year of performance would be 3.8 percent increase in the result (target 55.8 percent).
- Each subsequent year would continue to be set with a target using the most recent year´s data. This will account for smaller gains in subsequent years as performance improves toward the goal or measurement ceiling.
- Performing Provider Systems may receive less than their maximum allocation if they do not meet metrics and/or if DSRIP funding is reduced because of the statewide penalty).
DSRIP HIGH PERFORMANCE FUND
Who is eligible?
PPS, during a given performance period, that exceed their metrics & achieve high performance by:
- ✓ Exceeding a preset higher benchmark for reducing avoidable hospitalizations (ex. 20 percent gap to goal or the 90th percentile of the statewide performance); or
- ✓ Meeting certain higher performance targets for their assigned behavioral health population will be eligible for additional DSRIP funds from the high performance fund.
DSRIP HIGH PERFORMANCE FUND
Who decides where to set the high performance benchmarks?
- The state´s Quality and Measures Committee (QMC) will be responsible for setting the high performance target goals including the behavioral health high performance avoidable hospitalization threshold for bonus payment purposes.
- The QMC includes representatives from various sectors of healthcare including hospitals, behavioral health providers, nursing homes, managed care plans, provider organizations and consumer representation.
DSRIP HIGH PERFORMANCE FUND
How is the High Performance Fund financed?
- For Years 2–5, up to 10 percent of the total DSRIP funds from the Public Hospital Transformation Fund and Safety Net Performance Provider System Transformation Fund will be set aside to reward high performing systems.
- In addition, otherwise unrewarded funds will also be redirected to the high performance fund.
STATEWIDE ACCOUNTABILITY
We Are All In This Together!
STATEWIDE PERFORMANCE AND ACCOUNTABILITY
- Beginning in Year 3, limits on funding available and provider incentive payments may be subject to reductions based on statewide performance.
- Statewide performance will be assessed on a pass or fail basis for a set of four milestones.
- The state must pass all four milestones to avoid DSRIP reductions.
- If penalties are applied, CMS requires the state to reduce funds in an equal distribution, across all DSRIP projects.
- The DSRIP high performance fund will not be affected by any penalties.
STATEWIDE PERFORMANCE: MILESTONES
- Statewide performance on a universal set of delivery system improvement metrics as defined in Attachment J.
- Composite measure of success of projects statewide on project specific and population–wide quality metrics.
- Growth in statewide total Medicaid spending, including MRT spending, that is at or below the target trend rate, and growth in statewide total inpatient and emergency room spending at or below the target trend rate.
- Implementation of the state´s managed care contracting plan and movement toward a goal of 90 percent of managed care payments to providers using value–based payment methodologies.
DSRIP RESOURCES
DSRIP INFORMATICS PRODUCTS
- Data workbooks on Medicaid volume (claims/encounters, discharges and member counts by provider/region/county (non– PHI) developed by Salient available on the DSRIP website.
- Web Based Performance Dashboards with drillable data on member counts by region and baseline performance data (PQIs, PPRs, etc.) are under development by Salient and will be available on DSRIP website (planned for June).
- DSRIP Performance Portal (expected early fall) will have expanded capabilities for deeper dive analytics for DSRIP projects.
- Report submission capabilities are also being built into the expanded Health Home Portal.
SALIENT DATA WORKBOOKS
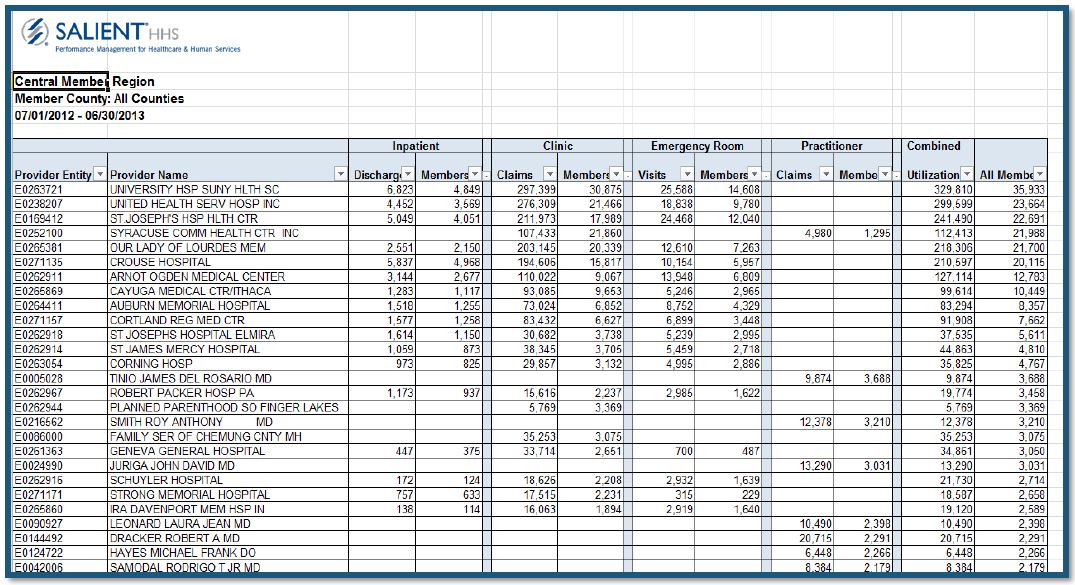
DSRIP METRIC WORKBOOKS
| Program––> | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Most Recent NYS MMC 2012 (or 2011*) | National NCQA Medicaid Mean | National NCQA Medicaid 90th Percentile | National NCQA Medicaid 10th Percentile | Comments | Metric | Metric Source | EBM Chronic Disease | CC & Tx Care |
| Metric –– Avoidable Events | ||||||||
| 6.79* | Per 100 At Risk Admissions | PPR Per 100 | 3M | x | x | |||
| 59.57* | Per 100 Eligible ER Visits | PPV (ED) | 3M | x | x | |||
| 11.23* | Per 100,000 Member Months | PQI# 1 (DM Short–term comp.) | AHRQ | x | x | |||
| NA | Per 100,000 Member Months | PQI# 2 (Perforated Appendix) | AHRQ | |||||
| 16.42* | Per 100,000 Member Months | PQI# 3 (DM long term comp.) | AHRQ | x | ||||
| 81.24* | Per 100,000 Member Months | PQI# 5 (COPD) | AHRQ | x | x | |||
| 11.04* | Per 100,000 Member Months | PQI# 7 (HTN) | AHRQ | x | x | |||
| 30.72* | Per 100,000 Member Months | PQI#8 (Cong. Heart Failure) | AHRQ | x | x | |||
| NA | Per 100,000 Member Months | PQI#9 (Low birth weight) | AHRQ |
DSRIP ONLINE VALUATION TOOL
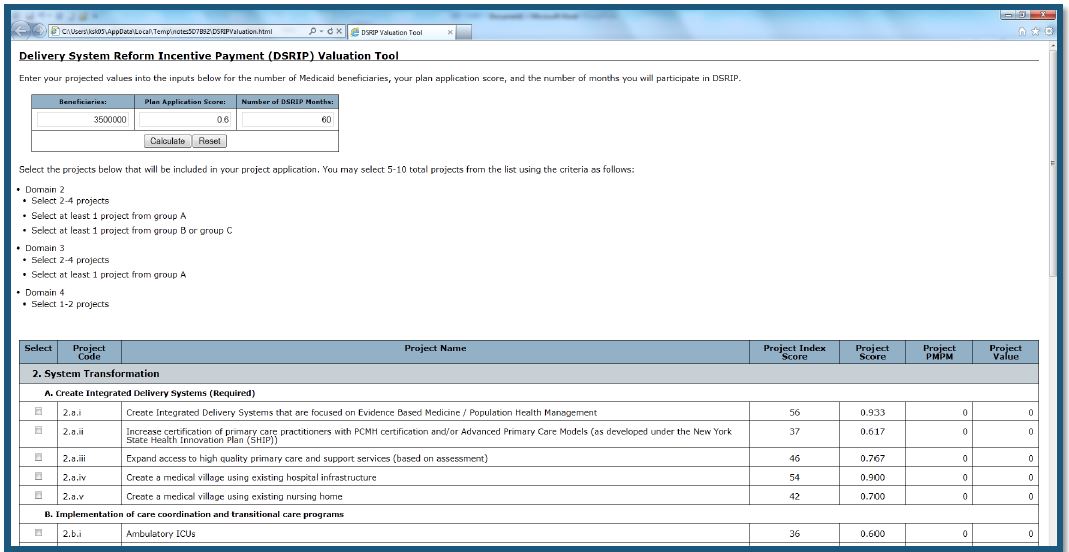
DSRIP WEBSITE
- Links to MRT Waiver Amendment Documents (STCs)
- DSRIP Glossary
- DSRIP Public Meeting Dates & Locations
- DSRIP Presentation
- DSRIP Toolkit
- DSRIP Valuation Tool
- Links to Performance Data
- DSRIP email address
- DSRIP FAQs...more to follow!
|top of section| |top of page|
INDEPENDENT ASSESSOR AND EVALUATOR
Key DSRIP Contractors
INDEPENDENT ASSESSOR
The state will contract with an independent entity with expertise in delivery system restructuring and improvement, project management, payment reform and with experience in implementation of statewide programs.
- Independent assessor will:
- ✓ Conduct a transparent and impartial review of all proposed DSRIP project plans;
- ✓ Make project approval recommendations to the state;
- ✓ Conduct a mid–point assessment of Project Plans;
- ✓ Manage Learning Collaboratives throughout the state; and
- ✓ Oversee ongoing monitoring of DSRIP projects including onsite visits.
INDEPENDENT EVALUATOR
The state will contract with an independent entity, with expertise in delivery system improvement and program evaluation, to serve as the evaluator of the DSRIP program.
- Independent evaluator will:
- ✓ Work in collaboration with the independent assessor;
- ✓ Assist with continuous quality improvement activities;
- ✓ Perform data analysis evaluation on clinical & population focused improvements; and
- ✓ Prepare a summative and final evaluation.
DSRIP TIMELINE
| Due Date/Submission Date | Activity/Deliverable |
|---|---|
| April – May 2014 | CMS approves STCs and DSRIP Attachments |
| New York posts the DSRIP Funding and Mechanics Protocol and the DSRIP Strategies Menu and Metrics for public comment for 30 days | |
| New York posts IAAF Qualifications and Application on for public comment for 14 days; | |
| 14–day IAAF application period begins once comment period closes | |
| IAAF awards can be distributed after 14 day application period closes | |
| State has 10 days to submit its first report for IAAF payments (STC 1(b)(iii)(A) of this section) | |
| State will make baseline data for DSRIP measures available | |
| State submits its proposed independent assess statement of work (SOW) for its independent assessor contract procurement | |
| May – July 2014 | State must accept DSRIP STCs or offer technical corrections, including for the DSRIP Operational Protocol and the Quarterly Reporting formats |
| State has 10 days to submit changes to the DSRIP Funding and Mechanics Protocol and the DSRIP Strategies Menu and Metrics once public comment period closes | |
| CMS will review changes to the DSRIP Funding and Mechanics Protocol and DSRIP Strategies Menu and Metrics and take action no later than 30 days after state submits changes | |
| State accepts DSRIP Design Grant applications and make Design Grant awards | |
| State posts DSRIP Project Plan Review Tool that independent assessor will use to score submitted DSRIP Project Plan applications for 30 days | |
| August 1, 2014 | State submits draft DSRIP evaluation design |
| August 30, 2014 | State submits its first quarterly report, including its operational report (STCs 35 & 36) |
| October 1, 2014 | State submits its Improved Management Controls report to CMS |
| State accepts DSRIP Project Plan applications | |
| State will perform initial review of submitted DSRIP Project Plan applications | |
| Independent assessor will perform full review of DSRIP project plan applications | |
| Independent assessor will post reviewed DSRIP Project Plan applications for public comment for 30 days |
DSRIP TIMELINE AFTER JANUARY 1, 2015
| New York Partnership Plan Renewal Period – January 1, 2015 |
|---|
| Independent assessor approval recommendations made public |
| State Distributes DSRIP Project Plan awards for approved performing provider systems |
| Quarterly Deliverables – Quarterly Report and Operational Report August 30, 2014; November 30, 2014; February 28, 2015; May 30, 2015 |
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT: STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT PROCESS
MRT WAIVER AMENDMENT: PUBLIC COMMENT PROCESS
New York is required to seek public comment on Attachments I and J. In addition, New York will seek public comment on the MRT Waiver Amendment STCs.
Public Comment periods:
- ✓ MRT Waiver Amendment STCs: (15 days)
- ✓ Attachments I and J public comment period: (30 days)
Public comment summaries and responses will be posted to the MRT website, and Attachments I and J will be updated (with CMS approval) based on public comment received.
DSRIP e–mail – dsrip@health.state.ny.us
PUBLIC MEETINGS
Five public meetings are being held throughout the answer questions and solicit comments from New Yorkers.
| Public Meeting Date | Time/Location |
|---|---|
| Rochester: Tuesday, April 15: | 8:30 a.m. – 11:30 a.m. University of Rochester, Memorial Art Gallery – Rochester |
| Syracuse: Tuesday, April 15: | 2:00 p.m. – 5:00 p.m. Crowne Plaza, Lafayette Room – Syracuse |
| Capital District: Wednesday, April 16 | 10:00 a.m. – 1:00 p.m. University at Albany, School of Public Health – Renselaer |
| NYC: Thursday, April 17 | 12:00 p.m. – 3:00 p.m. New York City College of Technology, Atrium Amphitheater – Brooklyn |
| Buffalo : TBD | TBD |
We want to hear from you!
DSRIP e–mail:
dsrip@health.ny.gov
´Like´ the MRT on Facebook:
http://www.facebook.com/NewYorkMRT
Follow the MRT on Twitter: @NewYorkMRT
Subscribe to our listserv:
http://www.health.ny.gov/health_care/medicaid/redesign/listserv.htm
|top of page|DSRIP:
Implications for Mental Health
Overview
- Performing Provider Systems (PPS) participating in the Delivery System Reform Incentive Payment (DSRIP) Program must choose between 5 and 10 projects geared toward system transformation, clinical improvement, and population health.
- Every PPS must select at least one project that focuses specifically on Behavioral Health (BH).
- Behavioral health populations can make the vital difference in helping PPSs reach targets in many system– wide projects that are not specifically geared to BH, as this population accounts for a disproportionate share of ER and inpatient admissions and re–admissions.
Mental Health Inpatient Readmissions
- 21.2% of individuals discharged from an inpatient mental health stay are readmitted within 30 days to the same or another inpatient facility.
| Region | Age Group | Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Statewide (Q1 and Q2 of 2013) |
Adults | 22.7% |
| Youth | 15.4% | |
| All Ages | 21.2% |
https://my.omh.ny.gov/analytics/
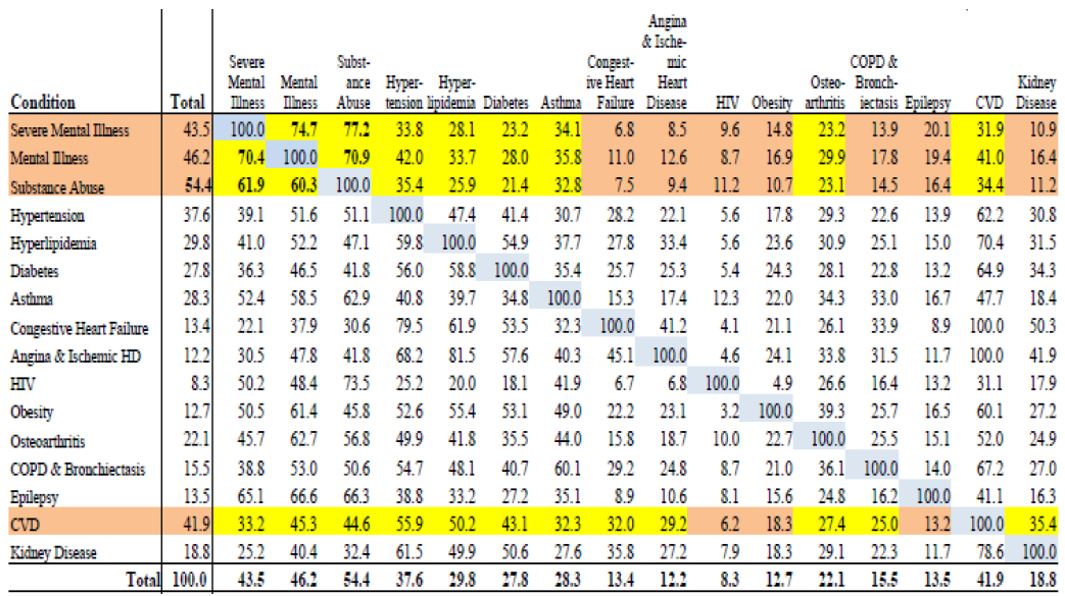
Health Home Highest Risk Populations
Multiple Co–Occurring Complex Conditions
Chronic Episode Diagnostic Categories
Health Home Eligibles Adults 21+ Years
With a Predictive Risk Score 75% or Higher (n=27,752)
Percent of Adult Recipients with Co–Occuring Condition
Domain 2 – System Transformation
- All DSRIP plans must include at least two projects from this domain based on their community needs assessment.
- All projects are evidence–based and person-centered, aiming to integrate services across systems.
- BH providers have an opportunity to participate as key players in these projects.
Project 2.a.i
Create Integrated Delivery Systems that are focused on Evidence Based Medicine / Population Health Management
- Expand access to high quality primary care, participate in payment reform, rebalance/restructure health delivery, and enhance community based services (especially behavioral health services).
- A comprehensive community needs assessment and an internal emphasis on quality improvement will direct project selection.
- BH providers and services are integral to the success of this project.
Project 2.b.iii
Emergency Department Triage for At–Risk Populations
- Care coordination and transitional care program will link patients with primary care, support patient confidence in understanding and self–management of health condition, improve provider communication, and assist transitioning members in the least restrictive environment.
- Given the high re–admission rate for BH populations, our providers will be necessary for the PPS to reach the targets for this project.
Project 2.b.iv
Care Transitions Intervention Model to Reduce 30 Day Readmissions for Chronic Health Conditions
- Provides a 30 day supported transition period after a hospitalization to ensure discharge directions are understood and implemented by the patients at high risk of readmission, particularly those with cardiac, renal, diabetes, respiratory and/or behavioral health disorders.
- BH co–morbidity with other chronic conditions creates an opportunity for our providers to have a substantial impact with this project.
Project 2.b.vi
Transitional Supportive Housing Services
- Participating hospitals will partner with community housing providers and, if appropriate, home care services to develop transitional housing for high risk patients who, due to their medical or behavioral health condition, have difficulty transitioning safely from a hospital into the community.
- Stable housing for the BH population will contribute to improved patient outcomes and support project goals.
Domain 3 – Clinical Improvement
All DSRIP plans must include at least two projects from this domain, based on their community needs assessment.
One required project from Sub–List A:
- Integration of primary care and behavioral health services
- Behavioral health community crisis stabilization services
- Implementation of evidence–based medication adherence programs (MAP) in community based sites for behavioral health medication compliance
- Development of withdrawal management capabilities within communities
- Behavioral Interventions Paradigm in Nursing Homes (BIPNH)
Domain 4: Population Wide Projects
- All DSRIP plans must include at least one project from this domain, based on their community needs assessment and the New York State Prevention Agenda.
- Must be consistent with selected Domain 3 projects.
- BH management is critical to all population based projects, encompassing both mental and physical health, as well as social determinants of health, including:
- Promoting mental, emotional and behavioral well–being in communities
- Preventing Substance Abuse and other Mental Emotional Behavioral Disorders
- Strengthening Mental Health and Substance Abuse infrastructure across systems
Links
DSRIP Information (DOH):
https://www.health.ny.gov/health_care/medicaid/redesign/delivery_system_reform_incentive_payment_program.htm
DSRIP Information (OMH):
https://www.omh.ny.gov/omhweb/special–projects/dsrip/
DSRIP Project Toolkit:
https://www.health.ny.gov/health_care/medicaid/redesign/docs/dsrip_project_toolkit.pdf
Mental Health service utilization by region:
http://bi.omh.ny.gov/cmhp/mh–services
BHO Phase I Performance:
https://www.omh.ny.gov/omhweb/special–projects/dsrip/bho.html
New York State Prevention Agenda:
http://www.health.ny.gov/prevention/prevention_agenda/2013–2017/index.htm
Follow Us