Generators and Heating Safety
When the power goes out, some people choose to use a generator to power a furnace, private well pump, or grinder pump. Others use a generator to run essential medical equipment and appliances. When there is no power, you may use alternate methods to heat your home. Always follow manufacturer instructions and follow the tips below to safely use generators and heaters.
Take steps to prevent carbon monoxide from fumes. They can cause carbon monoxide poisoning, even death. Install a carbon monoxide alarm. If it sounds, leave your home right away. Get more information about the dangers of carbon monoxide.
About Generators
Generators can be fueled by gas or propane. Choose a generator based on your personal and home needs. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions.
Plug appliances directly into a generator -- or, use a heavy-duty, outdoor-rated extension cord. Be sure it has watts/amps at least equal to the total of the appliance loads. If you choose to hardwire your generator, only a licensed electrician should install it into your household wiring system. It can be installed as either a portable or a permanent unit. An electrician should install a separate outdoor receptacle and a double-throw transfer switch. This will isolate the generator and protect utility workers repairing power lines. You should notify your electric company if you install this type of generator.
Safety Information 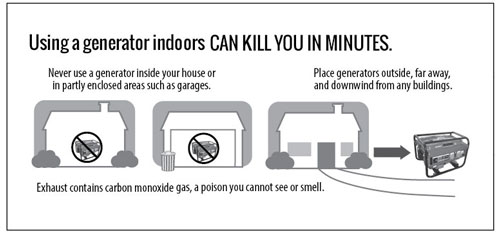
- • Generators should only be operated outside, far away from windows, doors, and vents. Never run a generator inside your home, basement, carport, crawlspace, or attached garage, even with ventilation. Carbon monoxide from the generator’s fumes can build up. This can lead to carbon monoxide poisoning, which can cause death. Get more information about dangers of carbon monoxide.
- Keep children away from generators at all times.
- Operate your generator according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Overloading your generator can damage it and your appliances. It can also cause a fire. Always install all recommended safety devices.
- Check the extension cord often to make sure it does not get hot while you’re using the generator. Stop using the generator right away if the extension cord gets hot. Never plug a generator into a wall outlet.
- If fuel is spilled on a hot generator, it can cause an explosion. If your generator has a detachable fuel tank, remove it before you refill it. If this is not possible, shut off the generator and let it cool before you refill the tank.
- Store gasoline away from the generator -- and not inside your home. Keep gasoline in properly labeled/color-coded storage containers. Improper storage can cause fires and explosions.
- Be careful about using an old or borrowed generator. If the manufacturer’s instructions are not followed, users may be at risk of carbon monoxide poisoning or overloading the unit.
Other Heating Sources
If you need to use an alternate source of heat, such as a fireplace, wood stove, or portable kerosene heater, be sure it is vented to the outside. Never use stoves or outdoor grills to heat your home. Without enough fresh air, carbon monoxide fumes can build up in your home and cause sickness or even death.
Get a Carbon Monoxide Alarm
Carbon monoxide (CO) is produced by burning fuels such as wood, oil, natural gas, propane, gasoline, and kerosene. Install battery-operated CO alarms or plug-in CO alarms with battery backup in your home. Follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions. If the CO alarm sounds, leave your home right away!